Are you curious about how Islamic finance manages to operate without charging or paying interest? If you’ve ever wondered why interest is considered forbidden in Islam and how banks still make profits without it, you’re not alone.
Islamic finance follows unique principles that protect you from exploitative lending while encouraging fairness and shared risk. You’ll discover the simple yet powerful ways Islamic banking avoids interest, ensuring your money grows ethically and responsibly. Keep reading to learn how these methods work and why they might change the way you think about finance forever.

Credit: academy.musaffa.com
Interest Prohibition In Islam
The prohibition of interest is a key principle in Islamic finance. It shapes how Muslims engage in financial transactions and investments. This rule is based on religious teachings and aims to promote fairness and justice in money matters.
Islamic finance avoids charging or paying interest. Instead, it uses other methods that share risk and profit. This approach supports a balanced economy and prevents exploitation.
Concept Of Riba
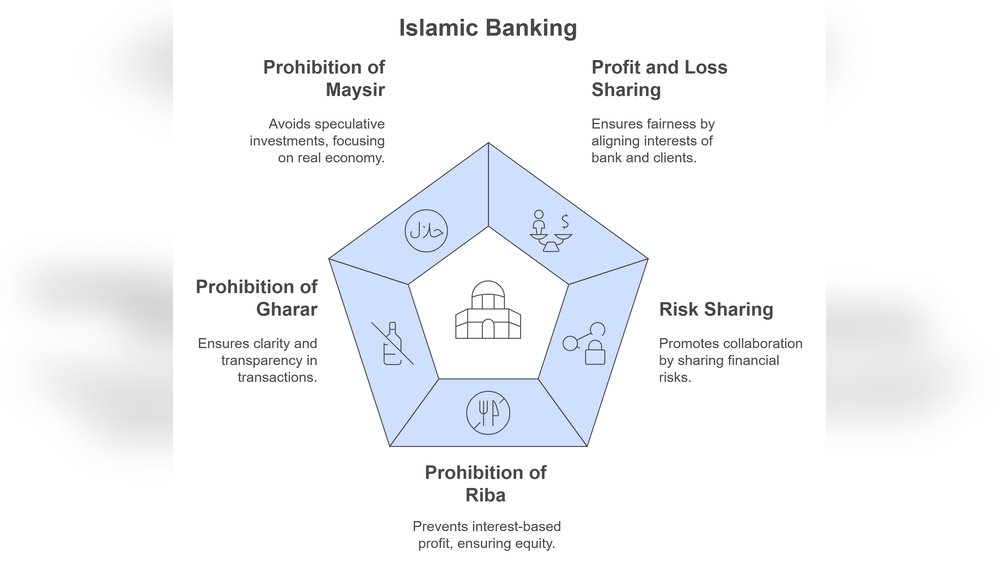
Riba means any guaranteed interest on loaned money. It includes extra charges beyond the original amount. Islam forbids riba to stop unfair gains from money alone. The focus is on real economic activity, not earning without effort.
Riba covers all forms of interest, whether small or large. This ensures fairness in all financial dealings. It encourages trade and investment based on shared risk.
Quranic Basis
The Quran clearly forbids riba in several verses. It calls riba unjust and harmful to society. The Quran warns that those who charge interest act against God’s commands.
One key verse says, “Allah has permitted trade and forbidden riba.” This shows the preference for honest business over interest. The teachings of Prophet Muhammad also emphasize this prohibition.
Economic And Social Impact
Prohibiting interest helps reduce wealth inequality. It stops the rich from earning money without effort. This protects poor and vulnerable people from debt traps.
Islamic finance promotes profit and loss sharing. Both parties share risks and rewards fairly. This creates a stable and ethical financial system.
The ban on interest also encourages productive investment. Money flows into real businesses and projects. This supports economic growth and benefits society as a whole.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/islamicbanking.asp-FINAL-a44177c529d24b97a0a4e857d65253cf.png)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
Principles Of Islamic Finance
Islamic finance follows clear principles that avoid interest, or riba. It promotes fairness and justice in financial dealings. These principles focus on shared responsibility and ethical practices. The goal is to create a balanced financial system that benefits all parties. Understanding these key principles helps explain how Islamic finance operates without interest.
Profit And Loss Sharing
Islamic finance encourages sharing both profit and loss. Investors and entrepreneurs share the risks and rewards together. This avoids guaranteed returns that come from interest. Instead, profits depend on the success of the business or investment. Losses are also shared, promoting fairness and cooperation.
Risk Sharing
Risk sharing is central to Islamic finance. Both parties in a transaction share the financial risks. This stops one side from gaining without effort or loss. Sharing risk creates trust and responsibility. It promotes careful decision-making and reduces unfair gain.
Ethical Investment
Islamic finance only supports ethical investments. It avoids businesses that harm society, like alcohol or gambling. Investments must follow moral and social guidelines. This ensures money supports positive and useful activities. Ethical investment protects the community and promotes good values.
Shariah-compliant Financial Instruments
Shariah-compliant financial instruments follow Islamic law to avoid interest, known as riba. These instruments focus on fairness, risk sharing, and ethical practices. They provide alternatives to conventional interest-based finance. Each instrument has unique features that align with Islamic principles.
Murabaha (cost-plus Financing)
Murabaha is a common Islamic financing method. The bank buys an item and sells it to the customer at a higher price. The customer pays this price in installments. The profit margin is agreed upon and fixed. This method avoids charging interest. It ensures transparency and fairness in transactions.
Mudaraba (profit-sharing Partnership)
Mudaraba is a partnership between a financier and an entrepreneur. The financier provides capital, while the entrepreneur manages the business. Profits are shared based on a pre-agreed ratio. Losses are borne by the financier alone. This encourages risk sharing and cooperation. It also avoids guaranteed interest returns.
Qard Hasan (interest-free Loan)
Qard Hasan is a benevolent loan given without any interest. The borrower repays only the principal amount. This type of loan aims to help those in need. It promotes social welfare and financial support without profit. The lender does not gain financially, making it fully Shariah-compliant.
Credit: www.premiumit.com
Islamic Banking Practices
Islamic banking practices follow strict rules to avoid interest, known as riba. These rules guide how banks handle money and offer services. The system focuses on fairness, risk-sharing, and ethical investing.
Banks use special contracts and partnerships. They share profits and losses with customers. This way, all parties benefit without charging or paying interest.
Interest-free Current Accounts
Islamic banks offer current accounts without paying interest. Customers can withdraw or deposit money anytime. The bank uses these deposits as interest-free loans. This is called qard. It helps the bank run without charging extra fees.
Account holders get full access to their money. The bank does not pay them any interest. This keeps the account halal and follows Islamic law.
Savings Accounts With Profit Sharing
Savings accounts in Islamic banks work differently. Instead of fixed interest, the bank invests the money. These investments follow ethical and shariah rules. Customers share in the profits or losses.
This profit-sharing model aligns the bank’s success with the customer’s. It promotes risk-sharing and avoids unfair gains. The returns depend on how well the bank’s investments do.
Halal Mortgages And Home Financing
Islamic mortgages avoid interest by using unique methods. The bank buys the property first. Then, it sells or leases the home to the buyer.
The buyer pays in installments without interest. The bank earns profit through rent or a higher sale price. This process follows Islamic rules and keeps the deal fair.
This system helps people own homes without breaking Islamic laws. It supports ethical financing and shared responsibility between bank and customer.
Avoiding Interest In Daily Finance
Avoiding interest in daily finance is essential in Islamic finance. Interest, known as riba, is prohibited because it exploits borrowers and causes inequality. Islamic finance uses ethical ways to manage money without charging or paying interest. This section explains practical steps to avoid interest in everyday financial matters.
Moving Funds To Shariah-compliant Accounts
One simple way to avoid interest is using Shariah-compliant accounts. These accounts do not earn or pay interest. Instead, banks may share profits from investments that follow Islamic rules. Depositors keep access to their money without involvement in interest-based earnings.
Shariah-compliant accounts help keep money safe and in line with Islamic principles. Many Islamic banks offer current and savings accounts that follow these rules. This choice supports ethical banking and respects religious beliefs.
Choosing Ethical Investments
Investing ethically is another key step to avoid interest. Islamic finance encourages investments in businesses that do not harm society or the environment. Avoiding companies involved in alcohol, gambling, or conventional finance is important.
Profit and risk are shared between investors and businesses. This approach avoids guaranteed returns, which could include interest. Ethical investments promote fairness and social responsibility while growing wealth.
Avoiding Conventional Interest-based Products
Many standard financial products involve interest, like conventional loans or credit cards. Islam teaches avoiding these products to prevent riba. Instead, Islamic finance offers alternatives such as profit-sharing loans or leasing agreements.
Islamic mortgages, for example, do not charge interest but use a rent or sale model. This way, people can buy homes without paying extra interest fees. Avoiding conventional interest products helps maintain financial integrity and religious compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Islamic Banking Avoid Interest?
Islamic banking avoids interest by using profit-and-loss sharing, ethical investments, and financing methods like murabaha and mudaraba. It prohibits riba, ensuring fair risk distribution and compliance with Shariah law.
How To Avoid Interest In Islam?
Avoid interest in Islam by using shariah-compliant accounts and Islamic finance models. Share profits and losses instead of earning fixed interest. Choose ethical investments and risk-sharing partnerships like murabaha or mudaraba to comply with Islamic principles.
How Do Muslims Get A Mortgage Without Interest?
Muslims get mortgages without interest through Islamic finance methods like murabaha or ijara. The bank buys the property and sells it at a profit or leases it. Payments occur in installments, avoiding interest, complying with Shariah law that prohibits riba (interest).
Why Does Islam Prevent Interest?
Islam forbids interest (riba) to prevent exploitation and wealth inequality. It promotes risk-sharing, ethical finance, and profit-loss sharing instead. This ensures fairness and financial stability, aligning with Islamic teachings against unfair gain and economic injustice.
Conclusion
Islamic finance avoids interest by using fair and ethical methods. It shares risk and profit between parties. This approach helps prevent debt traps and economic inequality. Banks invest in real assets, not just lending money for interest. Customers and banks work as partners, not creditors and debtors.
This system supports social justice and financial stability. It aligns with Islamic teachings against unfair gain. Understanding these principles shows how Islamic finance stays interest-free. It offers a clear alternative to conventional banking methods.