Are you curious about how partnerships can work without traditional loans or interest? Understanding the Mudarabah partnership could open new doors for your business or investment ideas.
This unique Islamic finance model lets one partner provide the capital while the other manages the business, sharing profits fairly. Imagine a partnership where risk and reward are balanced, and both parties benefit from success. You’ll discover exactly how Mudarabah works, why it might be the right choice for you, and what you need to know to get started.
Keep reading to unlock the secrets behind this powerful profit-sharing partnership.
Mudarabah Basics
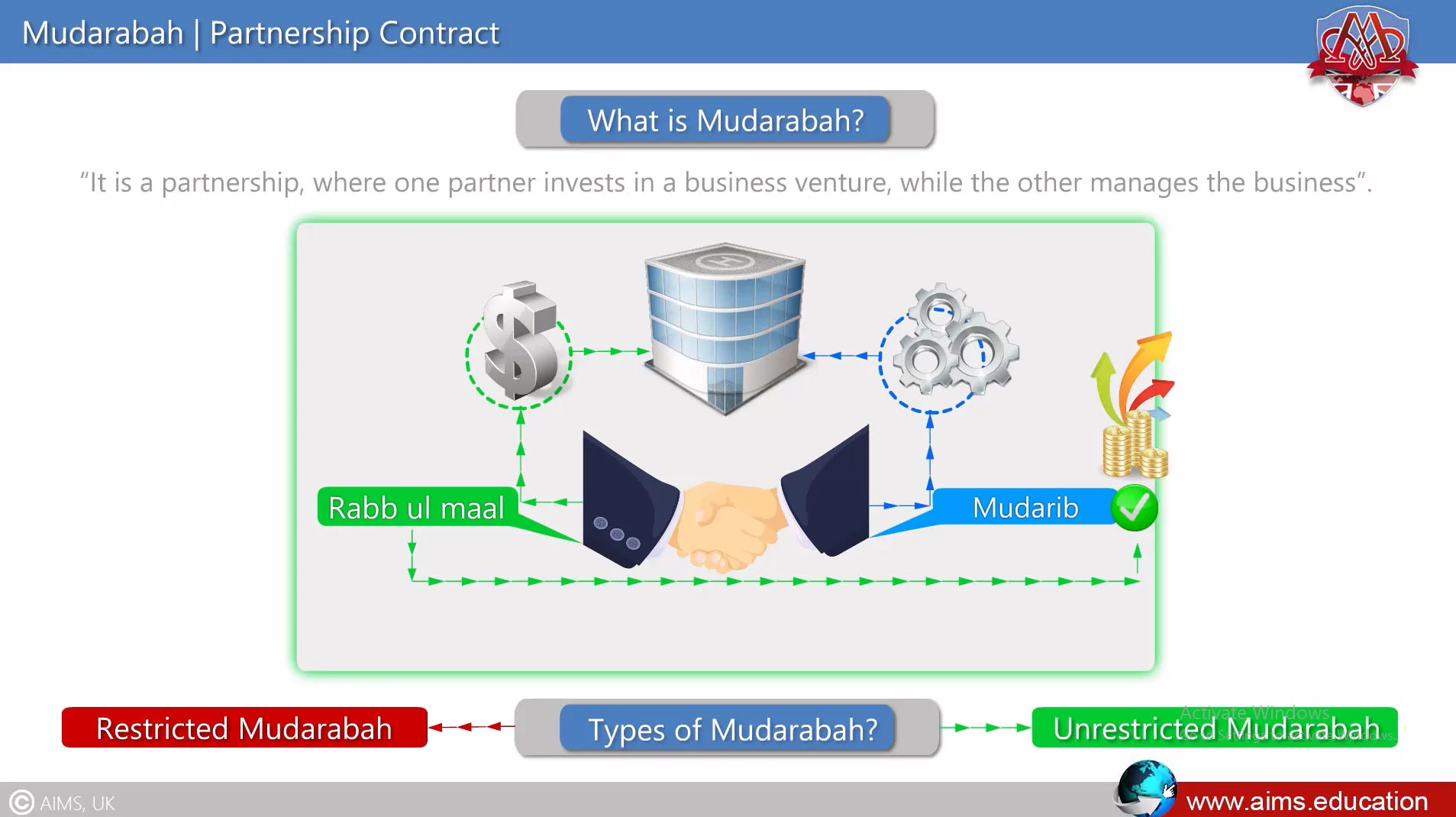
Mudarabah is a unique Islamic finance partnership. It combines capital and expertise to generate profit. One partner supplies the money. The other manages the business. Both share the profits based on a pre-agreed ratio. Understanding the basics helps grasp how this partnership works effectively.
Key Parties Involved
The partnership has two main parties. The first is the Rab al Mal, the investor who provides capital. The second is the Mudareb, the manager who runs the business. The investor trusts the manager to use the funds wisely. Both have clear, separate roles in the partnership.
Profit Sharing Mechanism
Profits are shared according to an agreed ratio. This ratio is decided before starting the venture. It can be equal or unequal. Both parties benefit only if the business makes a profit. This system motivates the manager to work hard and the investor to provide funds.
Loss Bearing Rules
Losses are handled differently than profits. The investor bears all financial losses. The manager loses time and effort but not money. This rule protects the manager from financial risk. It encourages the manager to focus on the business’s success.

Credit: www.slideteam.net
Types Of Mudarabah
Mudarabah partnerships come in different forms. Each type defines the roles and limits of the parties involved. Understanding these types helps partners manage their expectations and responsibilities clearly. The main division is between Restricted and Unrestricted Mudarabah. Each serves different business needs and risk levels.
Restricted Mudarabah
Restricted Mudarabah limits the activities of the working partner. The financier sets clear boundaries on how the funds are used. The working partner cannot invest outside these set terms. This type protects the investor from unwanted risks. It keeps the business focus narrow and controlled. Often used in projects with specific goals or sectors.
Unrestricted Mudarabah
Unrestricted Mudarabah allows the working partner full freedom to manage the funds. The investor trusts the partner’s skills and judgment. The working partner can invest in any profitable venture. This type suits experienced managers with good business sense. It encourages creativity and flexibility in running the business. Both parties share profits as agreed but bear losses differently.
Contract Essentials
The contract essentials form the foundation of a Mudarabah partnership. They define the rights and duties of both parties. Clear terms help avoid conflicts and ensure smooth cooperation.
Each element in the contract has a specific role. The capital provider and the manager must understand their commitments. This clarity promotes trust and fairness.
Capital Contribution
The capital provider supplies all the funds needed for the business. This money is the basis for the partnership’s operations. The amount and form of capital must be clearly stated. Only monetary capital is allowed, not services or labor.
The capital remains under the provider’s ownership. The manager cannot use it for personal purposes. Any losses are deducted from this capital, unless caused by manager’s negligence.
Management Role
The manager runs the business on behalf of both parties. They make daily decisions and handle operations. The manager must act honestly and with skill. They cannot delegate their management duties without permission.
The capital provider does not take part in managing the business. Their role is to provide funds only. The manager’s responsibility includes reporting progress regularly to the capital provider.
Profit Ratio Agreement
Profits from the business are shared according to a pre-agreed ratio. This ratio must be fixed at the start of the contract. It can be equal or uneven, depending on the agreement.
Losses, however, are borne only by the capital provider unless caused by the manager’s fault. This clear division helps both parties understand their financial risks and rewards.
Rights And Duties
In a Mudarabah partnership, understanding the rights and duties of each party is essential. This partnership involves two key players: the investor and the manager. Each has specific roles that ensure the success of the venture. Clear rights and responsibilities help maintain trust and fairness.
Investor’s Rights
The investor provides the capital for the business. They have the right to receive a share of the profits. The profit share is agreed upon before starting the partnership. The investor also has the right to monitor the business progress. They can request regular reports to stay informed. However, the investor does not take part in daily management.
Manager’s Responsibilities
The manager runs the business using the investor’s capital. They must work diligently and honestly. The manager must keep accurate records of all transactions. They must avoid any actions that can harm the business. The manager also has to share profits as agreed. Losses caused by the manager’s negligence are their responsibility.
Restrictions On Management
The manager cannot use the capital for personal purposes. They must not invest in projects outside the agreed terms. The manager cannot borrow money against the partnership’s assets. Any major decisions require the investor’s approval. These rules protect the investor’s funds and the partnership’s integrity. Respecting these limits builds a strong and trustworthy relationship.
Termination Conditions
Termination conditions define when and how a Mudarabah partnership ends. These rules protect both the investor and the manager. Understanding them helps avoid disputes and ensures smooth closure. The partnership can end voluntarily, upon expiry, or due to other agreed terms. Each condition has specific effects on the business and profit distribution.
Voluntary Ending
Either partner can end the Mudarabah voluntarily. They must give clear notice to the other party. Notice allows time to settle affairs and close the business. Ending voluntarily means no breach of contract occurs. Both partners share profits or losses up to the termination date. The manager stops purchasing new goods after notice.
Expiry Of Term
Some Mudarabah agreements set a fixed term. The partnership ends automatically when this term expires. No extra notice is needed for expiry termination. Partners review the final accounts and share the profits or losses. If they want to continue, they must create a new agreement. Expiry ensures a clear timeline for the partnership.
Effects Of Termination
Termination stops the manager from making new investments. Existing projects must be completed or sold off. Profits and losses are calculated up to the end date. The investor receives their capital back after settlement. Both partners lose rights to manage or control the business. Termination protects each partner’s financial interests clearly.
Applications In Finance
Mudarabah partnership is a key concept in Islamic finance. It combines capital from one party with expertise from another. This partnership shares profits based on a pre-agreed ratio. Losses are borne by the capital provider only. Mudarabah has many practical uses in finance. It supports various financial activities while following Islamic rules.
Investment Ventures
Mudarabah is widely used in investment projects. One partner provides the money. The other manages the business or investment. Profits are divided according to their agreement. This allows investors to fund ventures without managing daily operations. It encourages more people to invest in new ideas.
Banking Products
Many Islamic banks offer Mudarabah-based products. Savings accounts and investment accounts often use this model. Customers deposit money, and the bank invests it. Any profits are shared between the bank and customers. This system avoids interest, which is not allowed in Islam. It also builds trust between banks and clients.
Entrepreneurship Support
Mudarabah helps entrepreneurs start and grow businesses. Investors provide capital while entrepreneurs manage the work. Both share profits according to their deal. This reduces financial risks for new business owners. It also encourages innovation and job creation. Entrepreneurs gain access to funds without giving up full ownership.
Advantages For Partners
The Mudarabah partnership offers clear benefits for both parties involved. It allows investors and managers to work together with shared goals. Both gain from the success of the business. This creates a fair and motivating environment for all partners.
Risk Sharing Benefits
In a Mudarabah partnership, risks are shared fairly. The investor provides the capital and bears financial loss. The manager offers skills and effort but does not lose money. This balance lowers the burden on each partner. Both work hard to avoid losses and increase profits.
Access To Capital
The partnership allows managers to access needed funds. They can start or grow a business without full capital. Investors provide money while managers focus on running the business. This opens doors for new projects and ideas. It helps businesses expand with less financial strain.
Profit Opportunities
Profits are shared based on a pre-agreed ratio. Both investor and manager benefit from successful ventures. This creates strong motivation to work efficiently. Each partner gains from the business growth. It encourages trust and long-term cooperation.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Challenges And Risks
Mudarabah partnerships offer a unique way to share profits in business. Yet, they come with certain challenges and risks. Understanding these can help partners make better decisions.
Risks can affect the success and trust between the investor and manager. Each party must be aware of potential problems in this type of partnership.
Management Misconduct
The manager controls the business operations in Mudarabah. Misconduct or poor decisions by the manager can cause losses. Lack of transparency or dishonesty harms the investor’s trust. Monitoring the manager’s actions is difficult but very important.
Profit Estimation Issues
Profit sharing depends on accurate calculation of earnings. Estimating profits can be tricky due to market changes or false reporting. Disputes may arise if profits are not clear or fairly shared. Both parties should agree on clear methods to calculate profits.
Legal And Compliance Risks
Mudarabah must follow Islamic finance rules and local laws. Legal gaps or unclear contracts can cause problems later. Non-compliance with regulations can lead to penalties or business closure. It is vital to have proper legal advice and written agreements.
Comparing Mudarabah With Other Models
Understanding how Mudarabah compares to other financial models clarifies its unique features. It highlights its role in Islamic finance and shows how it differs from common partnerships and loans. Such comparisons help investors and entrepreneurs choose the right model for their needs.
This section explains key differences between Mudarabah, Musharakah, and conventional loans. Each model has distinct rules about profit, loss, and management roles.
Difference From Musharakah
Mudarabah involves two parties: one provides capital, the other manages the business. Only the manager invests effort, while the investor supplies funds.
In Musharakah, all partners contribute capital and share management duties. Both partners share profits and losses according to their investment ratio.
Mudarabah limits the investor’s role to funding only. Musharakah encourages active involvement from all partners.
Distinction From Conventional Loans
Conventional loans require fixed interest payments regardless of business success. The borrower must repay with interest even if profits are low or losses occur.
Mudarabah profits are shared based on a pre-agreed ratio. Losses are borne by the investor alone, unless caused by manager’s negligence.
Mudarabah avoids interest, aligning with Islamic finance principles. It creates a partnership rather than a debtor-creditor relationship.
Global Impact
The Mudarabah partnership has influenced finance beyond Islamic borders. It offers a unique way to share profits and risks. This concept supports businesses and investors globally. Its impact grows as more markets recognize its value. Understanding this impact helps grasp how Mudarabah shapes modern finance.
Adoption In Islamic Countries
Islamic countries widely accept Mudarabah as a core finance tool. It aligns with Shariah laws and ethical business practices. Banks and financial institutions use it to fund projects fairly. This partnership promotes entrepreneurship and economic growth. Many governments support Mudarabah to boost financial inclusion. It helps small and medium businesses access capital easily.
Integration In Conventional Finance
Conventional finance sectors show interest in Mudarabah principles. Some banks combine it with traditional banking products. This blend creates ethical investment opportunities for diverse clients. Mudarabah offers an alternative to fixed-interest loans. It reduces risk by sharing profits instead of charging fixed fees. Financial markets benefit from this flexible and fair structure.
Credit: aims.education
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Mudarabah Partnership?
Mudarabah partnership is an Islamic finance contract where one party provides capital and the other manages the business. Both share profits.
What Is The Concept Of Mudarabah?
Mudarabah is an Islamic finance partnership where one provides capital, the other manages the business, and both share profits.
Can Each Partner Terminate Mudarabah At Any Time?
Each partner can terminate Mudarabah anytime by giving notice. If set for a term, it ends automatically at term completion.
Can Each Partner Participate In The Management Of Business In Mudarabah?
In Mudarabah, only the managing partner (Mudareb) handles business management. The investor (Rab al-Maal) does not participate.
Conclusion
Mudarabah partnership offers a clear way to share profits fairly. One partner invests money, while the other manages the business. Both parties agree on profit shares before starting. Risks and rewards are shared, making it a balanced contract. This model supports trust and cooperation in business.
Understanding Mudarabah helps to choose the right partnership style. It suits those wanting ethical and transparent investment options. Keep these basics in mind for successful Mudarabah ventures.
