Are you curious about how finance works in a way that aligns with your values and beliefs? Islamic finance offers a unique approach based on clear, ethical principles that guide every financial decision.
Understanding these principles is essential if you want to see how money can be managed fairly and responsibly. You’ll discover the core ideas behind Islamic finance—principles that prioritize justice, transparency, and shared risk. By the end, you’ll not only grasp the basics but also see how these principles could impact your financial choices in powerful ways.
Ready to explore the foundation of a financial system that might change the way you think about money? Keep reading to unlock the secrets of Islamic finance.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Core Concepts
The core concepts of Islamic finance form the foundation of its unique system. These principles guide financial activities to ensure they align with Islamic law. They promote fairness, transparency, and social justice. Islamic finance aims to create economic stability and ethical growth.
Understanding these core concepts is essential to grasp how Islamic finance works. Each principle serves a specific purpose and reflects Islamic values. Together, they create a financial system that benefits individuals and communities.
Sharia Compliance
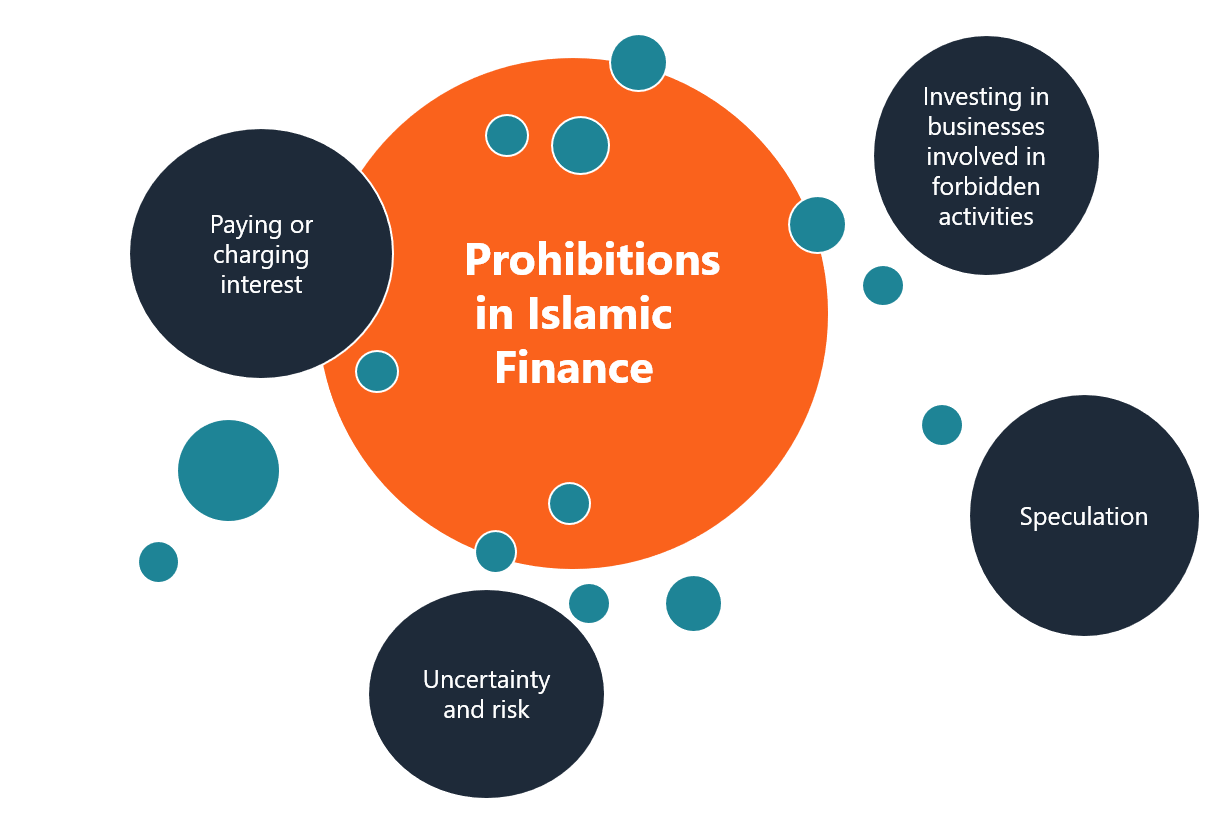
Sharia compliance means all financial transactions follow Islamic law. This law is derived from the Quran and the Sunnah. It prohibits activities that harm society or involve injustice. Financial products must avoid forbidden elements like gambling or uncertainty.
Risk Sharing
Risk sharing is a key feature of Islamic finance. Both parties in a contract share profits and losses. This approach encourages cooperation and fairness. It reduces the chance of one side bearing all risks alone.
Prohibition Of Interest
Charging or paying interest (riba) is forbidden in Islamic finance. Money should not generate money by itself. Instead, profit comes from real economic activity and trade. This rule prevents exploitation and unfair gain.
Asset-backed Financing
Islamic finance requires transactions to be backed by tangible assets. This links finance to the real economy. It avoids speculation and promotes responsible investment. Every deal must have a clear underlying asset or service.
Ethical Investments
Investments must follow ethical and moral standards. Islamic finance rejects businesses involved in alcohol, gambling, or harmful products. It encourages investments that benefit society and protect the environment. This ensures money supports positive growth.

Credit: fastercapital.com
Key Contracts
Key contracts form the backbone of Islamic finance. These contracts define how money and assets move while following Islamic law, known as Shariah. Each contract type has specific rules that ensure fairness and prevent interest, which is prohibited in Islam.
Understanding these contracts helps grasp how Islamic finance works in real life. They promote shared risk and ethical investments. Below are the main contracts used in Islamic finance.
Mudarabah
Mudarabah is a profit-sharing contract between two parties. One provides capital, and the other offers expertise and management. Profits are shared according to a pre-agreed ratio. Losses are borne by the capital provider only. This contract encourages entrepreneurship and risk-taking without interest.
Musharakah
Musharakah means partnership. All partners contribute capital and share profits and losses. Each partner has a say in managing the business. This contract promotes joint investment and cooperation. It aligns with the Islamic principle of shared risk and reward.
Murabaha
Murabaha is a cost-plus financing contract. The seller discloses the cost and adds a known profit margin. The buyer agrees to pay this price, usually in installments. This contract is used for purchasing goods or assets. It avoids interest by fixing profit upfront.
Ijara
Ijara means leasing. It involves renting an asset for a fixed period and payment. Ownership remains with the lessor, while the lessee uses the asset. At the end, the asset may be sold or transferred to the lessee. Ijara is similar to conventional leasing but without interest.
Sukuk
Sukuk are Islamic bonds that represent ownership in assets. Investors receive returns from the asset’s income, not interest. Sukuk funds are used for projects or investments following Shariah rules. They provide a way to raise capital while sharing risk and reward.
Ethical Wealth Building
Ethical wealth building is a key principle in Islamic finance. It guides Muslims to grow wealth responsibly and fairly. This approach ensures money serves the community and respects moral values. Wealth is not just for personal gain but to support social welfare and justice.
Social Justice
Islamic finance promotes fairness in wealth distribution. It fights against poverty and inequality. The system encourages investment in projects that help society. Wealth should benefit all, not just a few. This principle supports social harmony and peace.
Charitable Giving
Charity is a vital part of ethical wealth building. Muslims give a portion of their wealth as Zakat. This act helps the poor and needy. It cleanses wealth and promotes kindness. Giving supports community development and reduces hardship.
Sustainable Growth
Islamic finance values long-term growth over quick profits. Investments must avoid harm to people or the environment. Businesses should be responsible and mindful. This principle protects future generations. Sustainable growth ensures wealth stays beneficial and balanced.
Transparency And Fairness
Clear and honest dealings are essential in Islamic finance. All parties must understand the terms and risks. Hidden fees or deceit are forbidden. Fair contracts build trust and prevent disputes. Transparency supports ethical business and strong relationships.
Credit: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Comparison With Conventional Finance
Islamic finance differs from conventional finance in several key areas. These differences arise from Islamic law, known as Shariah, which guides financial practices. Understanding these distinctions helps grasp how Islamic finance promotes ethical and risk-conscious transactions. Below, we explore the main contrasts under key themes.
Interest Vs Profit Sharing
Conventional finance relies heavily on interest, known as riba in Islamic terms. Charging or paying interest is common in loans and savings. Islamic finance forbids interest and instead promotes profit sharing. Investors and entrepreneurs share profits or losses based on agreed ratios. This approach encourages fairness and cooperation between parties.
Risk Allocation
In conventional finance, risk often lies mainly with the borrower. Lenders expect fixed returns regardless of outcomes. Islamic finance requires risk-sharing between all participants. Both profits and losses are shared fairly. This system reduces exploitation and encourages responsible investment and management.
Compliance And Governance
Islamic finance follows strict Shariah compliance rules. Financial products must pass scrutiny by a Shariah board. Conventional finance does not have such religious oversight. Governance in Islamic finance ensures investments align with ethical and moral values. This adds transparency and trust for all parties involved.
Practical Applications
The principles of Islamic finance guide many financial activities today. These principles ensure fairness, transparency, and ethical conduct in money dealings. They apply to various financial products and services. This section explores how Islamic finance principles work in practice.
Banking Products
Islamic banking products avoid interest, which is called riba. Instead, they use profit-sharing and trade-based models. For example, in a Murabaha contract, the bank buys an item and sells it to the customer at a fixed profit. In Ijara, the bank leases assets to clients for a fee. These products meet the needs of customers while following Islamic rules.
Investment Funds
Islamic investment funds follow strict guidelines. They invest only in halal (permissible) businesses. These funds avoid companies involved in alcohol, gambling, or pork products. The funds also avoid excessive risk and uncertainty. Profit and loss are shared fairly among investors. This approach attracts many ethical investors worldwide.
Takaful Insurance
Takaful is a type of Islamic insurance based on mutual cooperation. Participants contribute to a pool of funds to help each other in times of need. The system avoids uncertainty and gambling, which are not allowed in Islam. Surplus funds are shared among participants or used for charitable causes. Takaful provides financial protection with Islamic values.
Challenges And Opportunities
The principles of Islamic finance face unique challenges and offer significant opportunities. These arise from the need to align financial activities with Sharia law. Navigating these challenges requires careful regulation, market understanding, and technological advancement.
Regulatory Environment
Regulation in Islamic finance varies widely across countries. This inconsistency creates hurdles for global growth. Many regions lack clear guidelines tailored to Islamic financial products. Strong regulatory frameworks can build trust and attract investors. Regulators must balance innovation with compliance to Sharia principles. Harmonizing rules internationally remains a key challenge.
Market Growth
The demand for Islamic finance is growing rapidly worldwide. More Muslims seek financial services that respect their beliefs. New markets in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East show great potential. Growth depends on education and awareness about Islamic finance benefits. Expanding product offerings can meet diverse customer needs. Increased participation by non-Muslims also boosts market size.
Innovation And Technology
Technology drives innovation in Islamic finance products and services. Digital platforms improve access and reduce costs for customers. Fintech solutions enable faster, transparent transactions aligned with Sharia rules. Blockchain and smart contracts hold promise for compliance and efficiency. However, adapting technology to Islamic principles requires careful design. Innovation can help Islamic finance compete globally.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The 5 Principles Of Islam?
The five principles of Islam, known as the Five Pillars, are Shahada (faith declaration), Salah (prayer), Zakat (charity), Sawm (fasting during Ramadan), and Hajj (pilgrimage to Mecca). These pillars guide a Muslim’s faith and daily practices.
What Are The 5 Principles Of Finance?
The five principles of finance are earning, spending, saving and investing, borrowing, and protecting assets.
What Is The Main Rule Of Islamic Finance?
The main rule of Islamic finance prohibits interest (riba) and promotes risk-sharing, ethical investments, and asset-backed transactions.
What Are The 5 Principles Of Shariah?
The 5 principles of Shariah are: justice, welfare, prevention of harm, freedom of contract, and public interest. These guide ethical and legal Islamic practices.
Conclusion
Islamic finance builds on fairness, transparency, and ethical values. It avoids interest and promotes risk-sharing. This system supports social justice and economic stability. Understanding its principles helps make informed financial decisions. Islamic finance offers an alternative way to manage money responsibly.
It aligns financial activities with moral and religious beliefs. Following these principles can lead to sustainable growth and trust. Embracing Islamic finance encourages ethical investments and community welfare. These core ideas shape a financial system rooted in faith and fairness.