Are you curious about how finance can work without interest or unethical investments? Shariah compliant finance offers a unique way to manage your money that aligns with Islamic principles.
It avoids charging or paying interest and steers clear of industries that harm society. Instead, it focuses on fairness through profit-sharing, partnerships, and leasing arrangements. If you want to understand how this system could impact your financial choices and open new opportunities, keep reading.
This guide will break down the basics clearly and show you why Shariah compliant finance is gaining attention worldwide. Your journey to smarter, ethical finance starts here.

Credit: amanieadvisors.com
Shariah Finance Basics
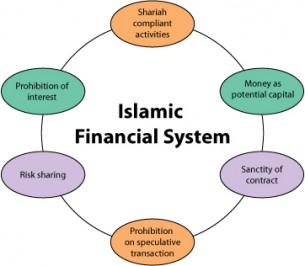
Shariah compliant finance follows rules set by Islamic law. It guides financial activities to be fair and ethical. This system offers an alternative to conventional finance, focusing on justice and social welfare.
Understanding its basics helps appreciate how it works. The principles ensure money is handled without harm or exploitation.
Core Principles
Shariah finance is based on justice, fairness, and transparency. It forbids activities that harm society or individuals. Contracts must be clear and agreed upon by all parties. Risk and reward are shared to promote cooperation.
Interest-free Model
Charging or paying interest is not allowed in Shariah finance. Instead, profit comes from trade and investment in real assets. This model encourages productive use of money. It avoids exploitation through unfair gains on loans.
Ethical Investment Criteria
Investments must follow ethical standards under Shariah law. Businesses involved in alcohol, gambling, or harmful products are not allowed. Investments should promote social good and avoid harm. This ensures funds support positive and responsible growth.
Credit: www.responsible-investor.com
Financial Instruments
Financial instruments in Shariah compliant finance follow Islamic law principles. They avoid interest and focus on fairness and transparency. These tools help businesses and individuals invest and manage money ethically. Each instrument has unique features aligned with Shariah guidelines.
Profit-sharing Contracts
Profit-sharing contracts, known as Mudarabah, involve two parties. One provides capital, and the other manages the business. Profits are shared based on a pre-agreed ratio. Losses, however, are borne by the capital provider only. This encourages trust and fairness between partners.
Leasing Agreements
Leasing agreements, or Ijarah, allow one party to lease an asset to another. The lessee pays rent to use the asset. Ownership remains with the lessor during the lease term. This arrangement avoids interest and promotes asset-based financing.
Joint Ventures
Joint ventures, called Musharakah, involve shared investment and management. Partners contribute capital and share profits and losses. Decisions are made jointly, ensuring cooperation and risk-sharing. This model supports business growth while respecting Shariah rules.
Wealth Growth Strategies
Wealth growth in Shariah compliant finance relies on strategies that respect Islamic principles. These strategies focus on ethical investment, protecting capital, and steady returns. They avoid interest and unethical business activities. This ensures investments align with faith and financial goals.
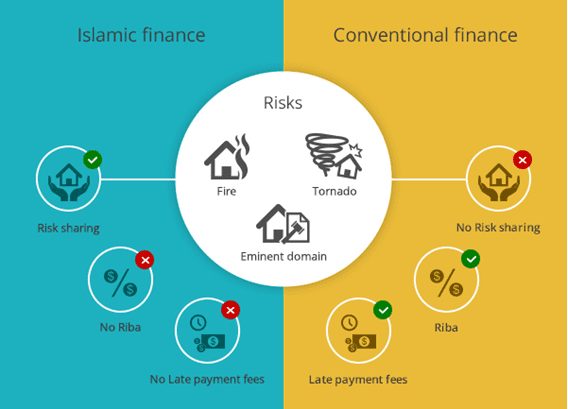
Risk Management Approaches
Managing risk is key to growing wealth without violating Shariah rules. Investors avoid excessive uncertainty and gambling. Contracts like Mudarabah (profit-sharing) spread risk fairly. Takaful, Islamic insurance, protects assets in a cooperative way. Risk is shared, not transferred to others unfairly.
Screening For Halal Investments
Screening removes investments in prohibited industries like alcohol, gambling, and pork. Companies must avoid high debt levels and interest income. Tools and guidelines help identify halal stocks and funds. This process ensures the portfolio stays pure and compliant with Islamic law.
Diversification Techniques
Diversification reduces risk by spreading investments across sectors and assets. Combining real estate, equities, and sukuk (Islamic bonds) balances returns. Avoiding concentration in one area protects from market swings. Diversified portfolios meet Shariah rules and improve long-term wealth growth.
Global Market Impact
Shariah compliant finance is making waves across global markets. It offers financial solutions aligned with Islamic law principles. These solutions appeal to a broad audience seeking ethical and interest-free finance. Its impact extends beyond Muslim-majority countries, influencing financial sectors worldwide.
Growth In The United States
The United States sees steady growth in Shariah compliant finance. More financial institutions now offer Islamic banking products. These products attract Muslim and non-Muslim customers alike. Demand rises for ethical investments and risk-sharing finance models. The market adapts by creating new compliant financial tools.
Adoption In Austin, Texas
Austin, Texas, emerges as a notable hub for Shariah compliant finance. Local banks and credit unions explore Islamic finance options. Entrepreneurs launch startups focused on halal financial services. The city’s diverse population supports this growth trend. Austin’s open market encourages innovative and inclusive financial products.
Challenges And Opportunities
Shariah compliant finance faces regulatory and educational challenges. Many lack awareness of its principles and benefits. Some regulations do not fully accommodate Islamic finance structures. Yet, opportunities exist in expanding financial inclusion. Collaboration between regulators and institutions can ease adoption. The future holds potential for wider acceptance and growth.
Legal And Regulatory Framework
The legal and regulatory framework shapes how Shariah compliant finance operates in the United States. Financial products must align with both Islamic principles and U.S. laws. This balance ensures that offerings meet religious standards and stay within legal boundaries. Understanding this framework helps investors and institutions navigate the complexities of Shariah finance.
U.s. Constitutional Limits
The U.S. Constitution forbids using any religion as the foundation for public law. This means Shariah law cannot govern courts or government policies. The Establishment Clause ensures laws remain secular. Religious beliefs can guide personal choices but cannot dictate public legal decisions. This creates a clear boundary between religion and state law.
State-level Legislation
Some states have passed laws limiting foreign or religious laws in their courts. These laws often target Shariah to prevent its influence in legal rulings. The goal is to keep state law consistent with American legal principles. Yet, these laws do not stop people from practicing their religion privately. The debate over these laws continues in various states.
Compliance In Financial Practices
Shariah compliant finance must follow both Islamic rules and U.S. regulations. Financial institutions must avoid interest and risky investments. They use profit-sharing and asset-backed contracts instead. Regulators require transparency and fairness in all transactions. This dual compliance protects customers and maintains market trust.
Credit: www.guidanceresidential.com
Common Misconceptions
Shariah compliant finance often faces many misunderstandings. These misconceptions confuse people about its principles and practices. Clearing these myths helps in better understanding this ethical finance model.
Below are some common misconceptions about Shariah compliant finance.
Shariah Vs. Secular Law
Shariah law is a religious legal system, not a state law. It guides Muslims on personal and financial matters. Secular law applies to everyone regardless of religion. Shariah compliant finance works within secular legal systems. It follows Islamic rules but respects national laws.
Interest Vs. Profit
Many confuse interest with profit in Shariah finance. Interest, called riba, is forbidden because it is fixed and unfair. Profit comes from sharing business risk and reward. Shariah finance uses profit-and-loss sharing instead of charging interest. This promotes fairness and partnership between parties.
Cultural Vs. Financial Aspects
Shariah finance is not just about culture or tradition. It is a financial system based on ethical rules. These rules ensure fairness, transparency, and social justice. People often mix cultural habits with financial laws. Understanding this difference helps avoid wrong assumptions.
Future Trends
The future of Shariah compliant finance looks promising and full of change. It will blend tradition with modern tools to serve more people worldwide. Innovations will make Shariah finance easier to access and more transparent. Ethical values will expand beyond Muslim communities. New partnerships will spread Shariah principles across borders.
Technological Innovations
Technology will reshape Shariah finance rapidly. Blockchain can ensure transparency and trust in transactions. Smart contracts will automate compliance with Islamic rules. Mobile apps will provide easier access to halal financial products. Artificial intelligence will help in risk assessment and decision-making. These tools will make Shariah finance faster and more user-friendly.
Expanding Ethical Finance
Shariah finance focuses on fairness and ethics. Its values will attract more people seeking ethical options. Green finance and social impact investing will grow within Shariah frameworks. More products will target sustainability and community development. This expansion will strengthen the role of ethical finance globally.
Global Collaboration
Countries and institutions will work together to promote Shariah finance. Standardizing regulations will ease cross-border investments. International organizations will support knowledge sharing and innovation. Partnerships will help develop new markets and financial products. Global collaboration will boost trust and acceptance of Shariah finance worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Shariah-compliant Financing?
Shariah-compliant financing follows Islamic law by prohibiting interest and investing in ethical, permissible activities. It ensures profit-sharing and risk-sharing.
What Is The 30% Rule In Islamic Finance?
The 30% rule in Islamic finance limits debt to 30% of a company’s total capital. This ensures financial stability and Shariah compliance.
Is Sharia Law Allowed In The Usa?
Sharia law cannot serve as public law in the USA due to the Constitution’s secular requirement. States may limit foreign or religious laws in courts. Muslims may practice Sharia privately, provided it does not conflict with U. S. laws.
Do Muslims Get 0% Interest?
Muslims do not earn or pay interest (riba) due to Islamic law. Instead, they use profit-sharing or fee-based financing methods.
Conclusion
Shariah compliant finance offers ethical and fair financial solutions. It avoids interest and promotes risk-sharing. Many people seek these options for personal and business needs. Understanding its principles helps make informed decisions. This finance model respects religious beliefs while meeting financial goals.
It grows steadily worldwide as awareness increases. Choosing Shariah compliant finance supports responsible and transparent money management. Explore these options to align finance with your values.
