Health insurance for self-employed individuals provides essential coverage and financial protection. It helps mitigate high medical costs and ensures access to healthcare.
Self-employed individuals often face unique challenges when securing health insurance. Without an employer-sponsored plan, finding affordable and comprehensive coverage can be daunting. Fortunately, there are several options available, such as individual health plans, Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), and plans through the Health Insurance Marketplace.
These options cater to different needs and budgets, ensuring that self-employed individuals can still access quality healthcare. Understanding these choices is crucial for maintaining both personal health and financial stability. By exploring available plans and benefits, self-employed professionals can make informed decisions about their health insurance needs.

Credit: insurancecenterhelpline.com
Importance Of Health Insurance
Health insurance is crucial for self-employed individuals. It provides financial security during medical emergencies. Without insurance, medical costs can be overwhelming. Having health insurance ensures you get the care you need without financial stress.
Financial Protection
Health insurance offers essential financial protection. Medical bills can be very high. Insurance helps cover these costs. This prevents debt from medical emergencies.
Here is a simple table to show potential costs:
| Medical Service | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Emergency Room Visit | $1,000 – $3,000 |
| Hospital Stay (per day) | $2,000 – $5,000 |
| Surgery | $10,000 – $50,000 |
With health insurance, these costs become manageable. You pay a small monthly premium. This is much less than unexpected medical bills.
Access To Quality Care
Health insurance ensures access to quality care. You can visit top doctors and hospitals. Insurance often covers preventive services. These include annual check-ups and screenings.
Here are some benefits of having health insurance:
- Regular check-ups
- Vaccinations
- Early diagnosis of diseases
- Access to specialists
Quality care means better health outcomes. It helps detect issues early. Early treatment is usually more effective and less expensive.
Types Of Health Insurance Plans
Choosing the right health insurance is vital for self-employed individuals. Understanding the types of health insurance plans can help you make an informed decision. Let’s dive into the different options available.
Individual Plans
Individual health insurance plans are designed to cover a single person. These plans are perfect if you don’t have dependents. They can be customized to meet your specific health needs. Here are some key benefits:
- Personalized coverage: Tailor the plan to suit your health requirements.
- Flexible premiums: Choose a plan that fits your budget.
- Comprehensive care: Access to a broad network of healthcare providers.
Some popular individual plans include HMOs, PPOs, and high-deductible health plans. Each offers different levels of coverage and flexibility.
Family Plans
Family health insurance plans cover multiple family members under one policy. These plans ensure that everyone in your family gets the care they need. Benefits of family plans include:
- Cost-effective: Often cheaper than buying individual plans for each family member.
- Unified coverage: Single deductible and out-of-pocket maximum for the whole family.
- Comprehensive benefits: Covers a wide range of medical services.
Family plans can be structured as HMOs, PPOs, or EPOs, each with unique features. You can choose based on your family’s specific health needs and budget.
| Plan Type | Key Features |
|---|---|
| HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) | Lower premiums, limited provider network, requires referrals for specialists. |
| PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) | Higher premiums, wider provider network, no referrals needed for specialists. |
| EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization) | Moderate premiums, limited provider network, no referrals needed for specialists. |
| HDHP (High-Deductible Health Plan) | Lower premiums, higher deductibles, often paired with an HSA. |
By understanding these types of health insurance plans, you can select the best option for your needs. Whether you choose an individual or family plan, make sure it provides the coverage you require.
Choosing The Right Plan
Self-employed individuals need tailored health insurance plans. Choosing the right plan can be overwhelming. This guide simplifies the process into key steps. Assess your needs, compare options, and find the best fit.
Assessing Needs
Identify your health requirements first. Do you need regular check-ups? Do you have chronic conditions? Make a list of your medical needs. Consider your family’s needs as well. This helps in finding a plan that covers everyone.
Ask these questions:
- How often do you visit the doctor?
- Do you need specialist care?
- What medications do you take?
- What is your annual healthcare budget?
Comparing Options
Once you know your needs, compare different plans. Look at premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs. Here’s a table to help:
| Plan | Monthly Premium | Deductible | Out-of-Pocket Maximum | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plan A | $200 | $1,000 | $6,000 | 80% |
| Plan B | $300 | $500 | $4,000 | 90% |
| Plan C | $150 | $1,500 | $7,000 | 70% |
Consider the network of doctors and hospitals. Are your preferred providers included? Look at the prescription drug coverage too. Does the plan cover your medications?
Read reviews from other self-employed individuals. Their experiences can offer valuable insights.
Costs And Premiums
Health insurance can be costly for self-employed individuals. Understanding costs and premiums can help manage your budget effectively. This section will break down the important aspects of monthly premiums and out-of-pocket expenses.
Monthly Premiums
Monthly premiums are the regular payments you make for your health insurance plan. These payments ensure that you have coverage when you need medical care. The amount you pay depends on several factors.
- Age: Older individuals usually pay higher premiums.
- Location: Your place of residence can affect your premium rates.
- Plan Type: Different plans offer varying levels of coverage and costs.
- Health Status: Those with pre-existing conditions might pay more.
Below is a sample table showing average monthly premiums by age group:
| Age Group | Average Monthly Premium |
|---|---|
| 18-29 | $200 |
| 30-39 | $300 |
| 40-49 | $400 |
| 50-59 | $500 |
| 60+ | $600 |
Out-of-pocket Expenses
Out-of-pocket expenses are costs that you have to pay yourself. These costs occur when you receive medical care. They include deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
- Deductibles: The amount you pay before your insurance starts to pay.
- Copayments: A fixed fee you pay for specific services, like doctor visits.
- Coinsurance: A percentage of the cost of a covered service you pay after meeting your deductible.
Understanding these expenses can help you choose the right plan. Consider your health needs and financial situation.
Tax Benefits And Deductions
Health insurance for self-employed individuals can be expensive. But, there are tax benefits and deductions that can ease the financial burden. Understanding these benefits can save you money.
Self-employed Health Insurance Deduction
The Self-Employed Health Insurance Deduction allows you to deduct your health insurance premiums. This deduction is available if you are self-employed and not eligible for employer-sponsored health insurance.
- You can deduct premiums for yourself, your spouse, and your dependents.
- The deduction is taken on Form 1040, reducing your adjusted gross income.
- This deduction can significantly lower your taxable income.
Health Savings Accounts
A Health Savings Account (HSA) is another way to save on health insurance costs. HSAs offer tax advantages and can be used to pay for qualified medical expenses.
- Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible.
- Funds in an HSA grow tax-free.
- Withdrawals for medical expenses are also tax-free.
| HSA Contribution Limits | Individual | Family |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $3,850 | $7,750 |
HSAs can help you save money and manage healthcare costs more effectively.
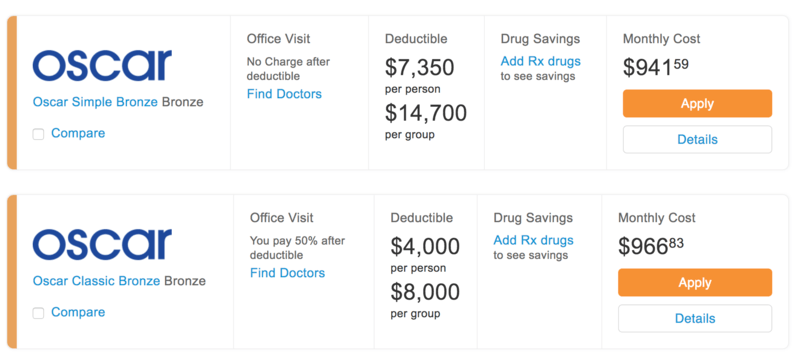
Credit: www.biglawinvestor.com
Tips For Managing Health Insurance
Managing health insurance can be challenging for self-employed individuals. With no employer to provide coverage, you need to take charge. Here are some tips to help you navigate health insurance effectively.
Regular Plan Review
Regularly review your health insurance plan. Plans change every year. Compare your current plan with new options. Look for changes in premiums, coverage, and benefits. Ensure your plan still meets your needs.
| Aspect | Things to Check |
|---|---|
| Premiums | Compare yearly costs |
| Coverage | Check what’s included |
| Benefits | Look for new benefits |
| Network | Ensure your doctors are in-network |
Utilizing Preventive Services
Preventive services can save you money. Most plans cover these services for free. Take advantage of annual check-ups, screenings, and vaccines. Regular check-ups can catch issues early. Early treatment is often less costly.
- Annual Check-ups: Visit your doctor once a year.
- Screenings: Get recommended tests for your age group.
- Vaccines: Stay up-to-date with vaccinations.
Using these tips can help you manage your health insurance better. Regular reviews and preventive care are key.

Credit: drnoorhealth.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Best Health Insurance For Self-employed?
The best health insurance varies by individual needs, budget, and coverage preferences.
Can Self-employed Get Affordable Health Insurance?
Yes, self-employed individuals can find affordable plans through the marketplace or associations.
Are There Tax Benefits For Health Insurance?
Yes, self-employed individuals can deduct premiums as a business expense, reducing taxable income.
How Do Self-employed Choose Health Insurance?
Consider factors like coverage, premiums, deductibles, and network providers to choose the best plan.
Is Short-term Health Insurance A Good Option?
Short-term health insurance can be a temporary solution but usually offers limited coverage.
Conclusion
Securing health insurance is vital for self-employed individuals. It safeguards against unexpected medical expenses. Research various plans to find the best fit. Prioritize coverage that meets your unique needs. Investing in health insurance ensures peace of mind and financial stability.
Make informed decisions to protect your health and livelihood.
