Are you curious about how Islamic finance offers a unique way to lease assets while staying true to Sharia principles? Islamic Leasing, or Ijarah, might be exactly what you need to understand.
Unlike conventional leasing, Ijarah is designed to align with your values by avoiding interest and promoting fairness. Whether you’re considering financing a home, car, or equipment, knowing how Ijarah works can open new doors for your financial decisions. Keep reading to discover how this ethical leasing method operates, its types, and real-life examples that can help you make informed choices with confidence.
Credit: aims.education
Basics Of Ijarah
Ijarah, or Islamic leasing, is a popular financing method in Islamic banking. It offers an ethical way to rent assets without involving interest. Understanding its basics helps grasp its value and usage.
This section explains what Ijarah means, its core principles, and how it differs from conventional leasing.
Definition And Key Features
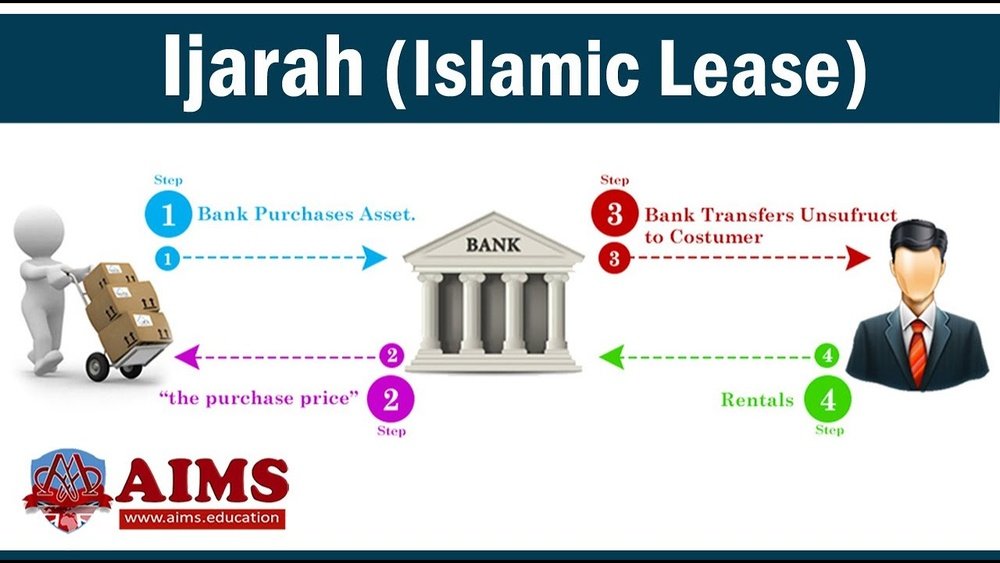
Ijarah means leasing or renting in Arabic. It involves a contract where the owner lets another person use an asset. The user pays rent for a fixed period.
The lessor keeps ownership of the asset. The lessee only gets the right to use it. The contract must clearly state the rent and lease duration.
Ijarah can cover property, vehicles, equipment, or services. The lessor must maintain the asset during the lease term.
Shariah Principles Behind Ijarah
Ijarah follows Islamic law, which forbids interest or “riba.” The rent is not interest but payment for asset use. Ownership stays with the lessor, avoiding unjust gain.
The contract must be fair and transparent. Both parties agree freely without coercion. The asset must exist and be usable during the lease.
Risk and responsibility lie with the lessor. This ensures justice and protects the lessee’s rights.
Difference From Conventional Leasing
Conventional leasing may include interest charges and transfer ownership risks differently. Ijarah separates ownership from usage rights clearly.
Interest is prohibited in Islamic leasing. Rent reflects real asset value and use, not interest or penalties.
The lessor maintains the asset in Ijarah, unlike some conventional leases. This protects the lessee from hidden costs.

Credit: fastercapital.com
Types Of Ijarah Contracts
Ijarah contracts offer flexible leasing solutions under Islamic finance rules. These contracts cater to different needs while complying with Shariah law. Understanding the main types of Ijarah contracts helps in choosing the right one for specific financial goals.
Each type varies in ownership transfer, payment structure, and contract duration. They serve individuals and businesses seeking ethical and interest-free leasing options. The three primary types are Operating Ijarah, Ijarah Muntahia Bitamleek, and Ijarah Thumma Al Bai.
Operating Ijarah
Operating Ijarah is a simple lease agreement. The lessor owns the asset and leases it for a fixed period. The lessee pays rent to use the asset without ownership rights. At the end, the asset returns to the lessor. This type suits short-term leasing needs.
Ijarah Muntahia Bitamleek (lease To Own)
This contract combines leasing with ownership transfer. The lessee rents the asset and gradually gains ownership. Ownership transfers after all payments complete or at contract end. It suits long-term financing like home or vehicle purchases. This method aligns with Islamic principles of fairness.
Ijarah Thumma Al Bai (lease Then Sale)
This type involves leasing followed by a sale agreement. First, the asset is leased to the lessee. Later, the lessee buys the asset at an agreed price. This contract separates lease and sale into two steps. It helps those who want to lease before buying.
How Ijarah Works In Practice
Ijarah, or Islamic leasing, follows clear steps to comply with Shariah rules. It involves leasing an asset, not selling it, ensuring both parties benefit fairly. The process protects rights and duties of lessor and lessee. Understanding how Ijarah works helps businesses and individuals use it confidently.
Process Flow In Islamic Leasing
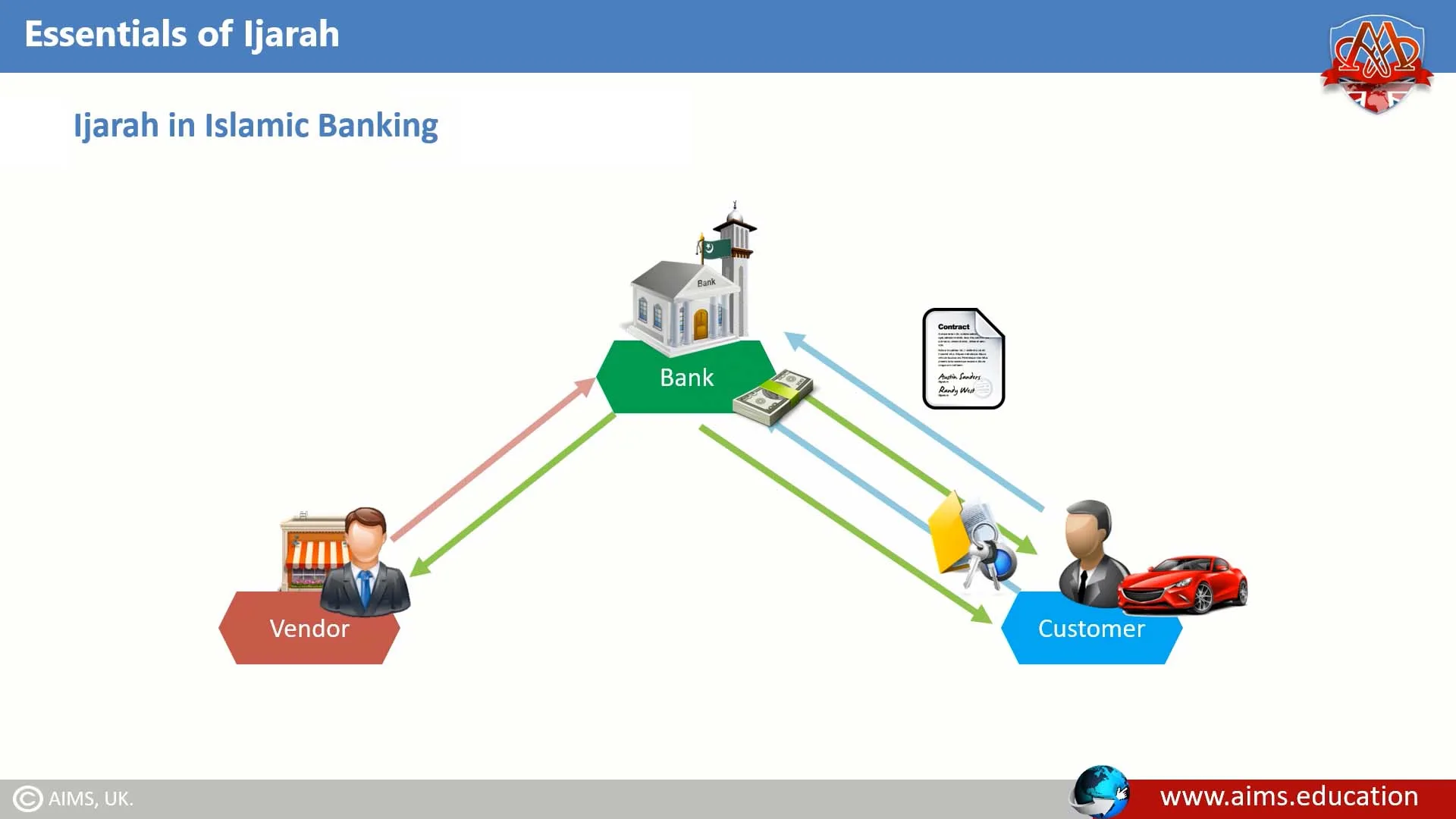
The lessor first buys the asset requested by the lessee. The ownership stays with the lessor during the lease term. The lessee uses the asset and pays rent agreed in advance. The lease period is fixed and clearly defined. At lease end, the asset may return to lessor or transfer to lessee. All terms must follow Islamic law and avoid interest.
Roles Of Lessor And Lessee
The lessor owns the asset and rents it out. They must maintain the asset in good condition. The lessee has the right to use the asset. They pay rent regularly and use the asset responsibly. Both parties agree on lease terms before starting. The lessor cannot charge extra fees beyond rent. The lessee cannot damage or misuse the asset.
Asset Selection And Usage Rights
The asset must be halal and usable for the lessee’s needs. Both parties agree on asset type and condition. The lessee gets the asset’s benefits but not ownership. Usage rights last only for the lease duration. The asset must be maintained well and used fairly. Any damage beyond normal wear is the lessee’s responsibility.
Benefits Of Ijarah Financing
Ijarah financing offers a unique way to lease assets while following Islamic principles. This method benefits both individuals and businesses by providing ethical financial solutions. It supports economic growth without compromising religious beliefs.
Using Ijarah financing helps avoid interest, which is prohibited in Islam. It focuses on fairness and transparency, making it a trusted choice for many. The structure of Ijarah contracts allows for clear terms and mutual agreement between parties.
Shariah Compliance Advantages
Ijarah financing strictly follows Shariah law. It avoids interest (riba) and uncertainty (gharar). This ensures the contract is ethical and acceptable in Islamic finance. The asset is leased, not sold, keeping the transaction halal. This compliance builds trust among Muslim clients.
Flexibility In Asset Acquisition
Ijarah allows leasing of many asset types. It can be real estate, vehicles, or equipment. Clients choose the asset they need without upfront purchase costs. The leasing period and terms can be tailored to fit budgets. This flexibility helps manage cash flow better.
Risk Sharing And Cost Transparency
The lessor retains ownership risk during the lease. This means maintenance and major repairs are usually the lessor’s responsibility. The lessee pays a fixed rental amount, clear from the start. This transparency prevents hidden fees and surprises. Both parties share risks fairly, creating balanced agreements.
Common Uses Of Ijarah
Ijarah is a popular Islamic leasing method. It helps people use assets without owning them at first. Many individuals and businesses use Ijarah for different purposes. This section explains common uses of Ijarah and how it supports various financial needs.
Real Estate Financing
Ijarah allows people to lease homes or commercial buildings. The leasing party uses the property while paying rent. It helps those who cannot buy real estate immediately. Businesses also use Ijarah to rent office spaces or shops. This way, they avoid large upfront costs and manage cash flow better.
Vehicle And Equipment Leasing
Many use Ijarah to lease cars, trucks, or machinery. It suits businesses needing equipment without buying it. Leasing vehicles reduces financial pressure for small companies. It also helps individuals who want a car without a loan. Ijarah contracts specify the lease period and rent clearly.
Business And Project Financing
Ijarah supports business growth by leasing tools or machines. It funds projects by providing assets needed for work. Companies can lease heavy equipment or technology for specific tasks. This avoids large capital investment and lowers financial risk. Ijarah keeps businesses flexible and financially stable.
Comparison With Other Islamic Contracts
Understanding Islamic Leasing (Ijarah) becomes clearer when compared to other Islamic contracts. Each contract serves distinct purposes and follows specific rules under Shariah law. Comparing Ijarah with Murabaha, Musharakah, and conventional leases highlights its unique features. This helps individuals and businesses choose the right financial solution.
Ijarah Vs Murabaha
Ijarah is a lease contract where the bank owns the asset. The customer pays rent to use it. Murabaha is a cost-plus sale agreement. The bank buys an asset and sells it to the customer at a marked-up price. In Ijarah, ownership stays with the lessor during the contract. In Murabaha, ownership transfers to the buyer after sale.
Ijarah focuses on renting the asset’s use. Murabaha focuses on asset purchase and resale. Payments in Ijarah are rental fees. In Murabaha, payments cover the asset’s price and profit margin. Ijarah suits short-term use needs. Murabaha suits those who want to own the asset.
Ijarah Vs Musharakah
Musharakah is a partnership contract where both parties share ownership. Profits and losses are divided based on agreed ratios. Ijarah involves no shared ownership. The lessor alone owns the asset. The lessee only pays rent for usage.
Musharakah requires joint management and risk sharing. Ijarah assigns maintenance and risk mainly to the lessor. Musharakah is ideal for joint investment projects. Ijarah fits leasing or renting needs without ownership change.
Ijarah Vs Conventional Lease
Conventional leases often involve interest, which is not allowed in Islam. Ijarah avoids interest by charging a fixed rent for asset use. Conventional leases may transfer ownership at the end. Ijarah can include a separate sale agreement for ownership transfer.
Ijarah follows strict Shariah principles, avoiding uncertainty and prohibited elements. Conventional leases focus on financial returns without religious restrictions. Ijarah offers a transparent, ethical leasing option. Conventional leases offer more flexibility but may include interest and risk.
Challenges And Considerations
Islamic Leasing, known as Ijarah, offers a unique financial solution based on Shariah principles. Despite its benefits, it faces several challenges that affect its growth and adoption. Understanding these challenges helps businesses and individuals make informed decisions.
Regulatory And Legal Issues
Regulations for Ijarah vary across countries. Some places lack clear Islamic finance laws. This creates uncertainty for providers and clients. Legal systems often favor conventional leases. It complicates enforcing Ijarah contracts. Compliance with both Shariah and local law is essential but difficult. This can slow down contract approval and execution.
Asset Ownership And Maintenance
In Ijarah, the lessor owns the leased asset. This means the lessor must maintain it. Proper upkeep is crucial to avoid disputes. The lessee uses the asset but cannot alter ownership rights. Defining responsibilities clearly in the contract is vital. Maintenance costs can be high, impacting profitability. Both parties must agree on terms for repairs and insurance.
Market Acceptance And Awareness
Many people still do not understand Ijarah fully. Lack of awareness limits its market reach. Some customers prefer conventional leasing due to familiarity. Banks and businesses must educate clients about Ijarah benefits. Building trust takes time and effort. Increasing knowledge can lead to wider acceptance and use.
Future Trends In Ijarah Finance
The future of Ijarah finance holds promising opportunities. It continues to evolve with shifts in technology and market demands. Islamic leasing adapts to global financial trends while staying true to Shariah principles.
New tools and platforms will enhance the efficiency of Ijarah contracts. More people and businesses seek ethical finance options. The integration of digital solutions will make Ijarah more accessible worldwide.
Technological Innovations
Technology plays a key role in shaping Ijarah finance. Smart contracts on blockchain ensure secure, transparent leasing. Automation reduces paperwork and speeds up approvals. Artificial intelligence helps assess risks and match clients with assets. These tools improve trust and lower costs for all parties.
Growing Global Demand
Demand for Shariah-compliant finance grows across continents. Muslim populations in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East increase. Non-Muslims also show interest in ethical leasing solutions. Small and medium businesses prefer Ijarah for asset financing. This demand encourages more financial institutions to offer Ijarah products.
Integration With Digital Finance
Ijarah integrates smoothly with digital banking and fintech services. Mobile apps allow clients to manage leases anytime, anywhere. Online marketplaces connect lessors and lessees directly. Digital payments simplify rental transactions and record keeping. These advances make Ijarah finance more user-friendly and efficient.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Islamic Leasing (ijarah)?
Islamic Leasing, or Ijarah, is a Sharia-compliant contract where the lessor leases an asset to the lessee for a fixed rent and period. Ownership remains with the lessor, while the lessee benefits from asset usage without interest-based financing.
How Does Ijarah Differ From Conventional Leasing?
Ijarah complies with Islamic law by avoiding interest (riba). Unlike conventional leasing, it focuses on asset usage and rent. The lessor retains ownership, and all terms align with Sharia principles, making it ethical and transparent for Muslims.
What Are Common Types Of Ijarah Contracts?
Common Ijarah types include Ijarah Thumma Al-Bai (lease followed by sale) and Ijarah Muntahia Bitamleek (lease ending with asset ownership). These structures provide flexible leasing and ownership options while adhering to Islamic finance rules.
Who Benefits Most From Ijarah Financing?
Individuals and businesses seeking Sharia-compliant financing benefit most. It suits those who want to use assets without interest, such as homes, vehicles, or equipment, while ensuring ethical financial practices aligned with Islamic principles.
Conclusion
Islamic Leasing, or Ijarah, offers a clear, fair way to lease assets. It follows Islamic law by avoiding interest and sharing risk. Both lessor and lessee benefit from transparency and agreed terms. This system supports many needs, from homes to equipment.
Understanding Ijarah helps people choose ethical financing options. It remains a trusted choice in Islamic banking worldwide.