Are you curious about how Islamic finance supports large projects like building homes or factories while staying true to Sharia principles? The Istisna contract could be the key to understanding this unique approach.
It’s a special agreement that allows you to finance the creation of an asset before it even exists, making it ideal for construction and manufacturing. If you want to know how this contract works, why it’s different from conventional financing, and how it can benefit your financial ventures, keep reading.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to grasp Istisna in Islamic finance, helping you make smarter decisions aligned with your values.
Credit: aims.education
Istisna Contract Basics
The Istisna contract plays a vital role in Islamic finance. It allows the financing of manufacturing or construction projects. This contract suits industries where goods are made on demand. Understanding its basics helps grasp its practical use and benefits.
Definition And Meaning
Istisna means “requesting to manufacture” in Arabic. It is a contract where a buyer orders an asset. The asset is built or manufactured later. The payment can be made in advance, in parts, or after delivery. This contract follows Islamic law, avoiding interest and uncertainty.
Key Features
Istisna involves a specific product made to order. The delivery time is agreed upon by both parties. Payment terms are flexible and can be scheduled. The manufacturer must deliver the exact item requested. This contract supports projects like building houses or making machinery.
Comparison With Other Contracts
Istisna differs from Salam, which is for agricultural goods. Salam requires full payment upfront, but Istisna allows flexible payment. Unlike Ijarah, which is a lease contract, Istisna deals with manufacturing. It also differs from Murabaha, where goods already exist. Istisna suits custom-made products with agreed specifications.
How Istisna Works
Understanding how Istisna works is key to grasping its role in Islamic finance. It is a unique contract used mainly for manufacturing or construction projects. This contract allows a buyer to order a product that does not yet exist. The seller agrees to produce and deliver the item at a future date. The process involves clear terms and conditions to ensure both parties are protected.
Contract Formation
The Istisna contract begins with an agreement between the buyer and seller. They must specify the product details, quality, and delivery date. Both parties agree on the manufacturing process and specifications. The contract is flexible, allowing changes if both sides consent. This ensures the product meets the buyer’s needs before production starts.
Payment Structures
Payment in Istisna can follow several methods. The buyer may pay in full upfront, in installments, or after delivery. This flexibility helps accommodate different financial situations. The payment terms must be clear in the contract to avoid disputes. Sharia-compliant financing rules guide these payments, avoiding interest or uncertainty.
Delivery And Completion
The seller is responsible for completing the product by the agreed date. Delivery can happen in stages or as a whole. The buyer inspects the product upon delivery to ensure it matches the contract. If the product meets the agreed standards, the transaction is complete. This process ensures transparency and trust between both parties.
Types Of Istisna Contracts
Istisna contracts have different types, each serving specific needs in Islamic finance. Understanding these types helps businesses and financiers choose the right contract. The main types are Classical Istisna and Parallel Istisna. Both types follow Islamic principles but differ in structure and application.
Classical Istisna
Classical Istisna is a basic contract where a buyer orders a manufacturer to produce a specific item. The product is made according to agreed specifications. Payment can be made in advance, during production, or after delivery. This type supports projects like construction and manufacturing. It allows customization and flexibility in payment terms. Both parties agree on delivery time and product details before starting.
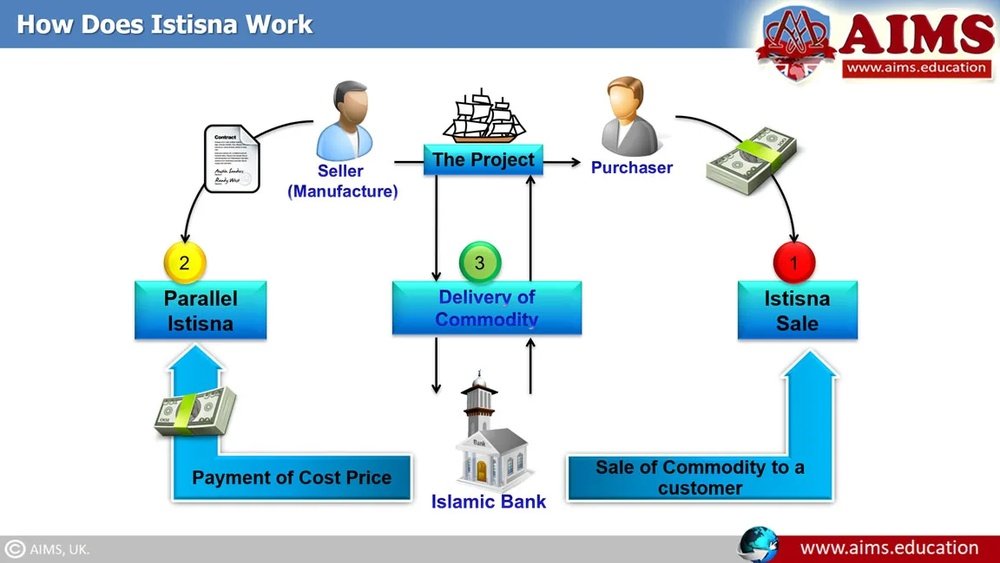
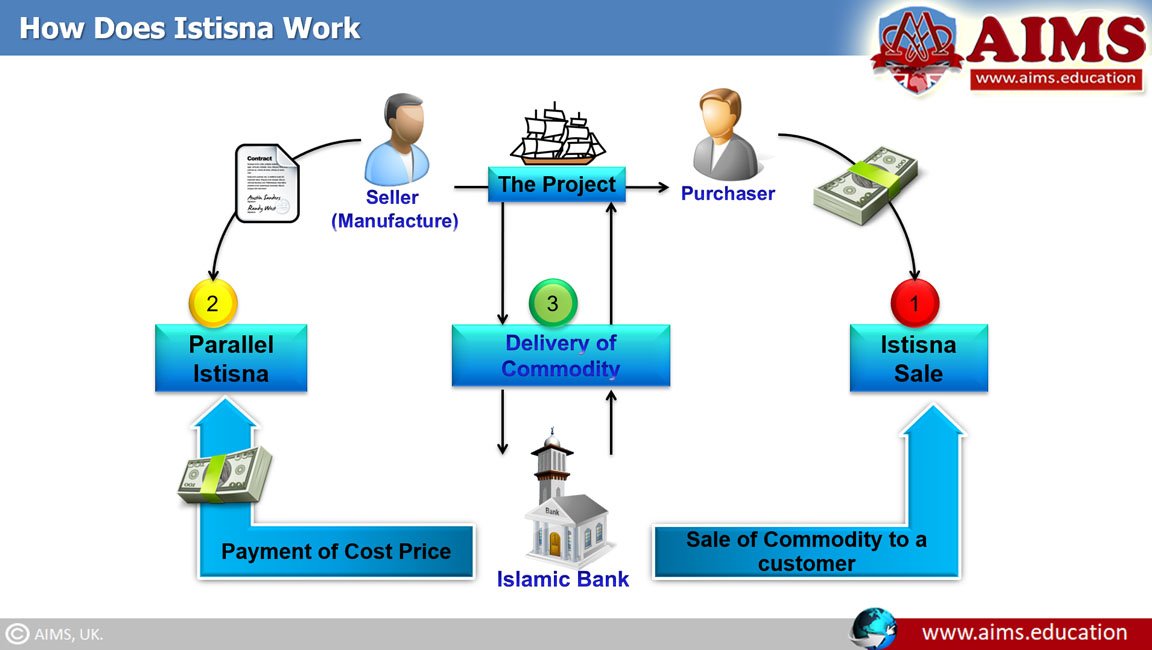
Parallel Istisna
Parallel Istisna involves two linked Istisna contracts. The first contract is between the financier and manufacturer. The second is between the financier and the buyer. The financier acts as a middleman, ordering the product and then selling it to the buyer. This type helps financiers manage risks and liquidity. It is common in large-scale projects and trade financing. Parallel Istisna ensures smooth transaction flow and clear roles for all parties.

Credit: cbonds.com
Benefits Of Istisna
Istisna contracts offer several key benefits in Islamic finance. These advantages make Istisna a preferred choice for many businesses and individuals. It supports ethical trade and meets specific financial needs. Understanding these benefits helps to appreciate its role in Islamic banking and finance.
Sharia Compliance
Istisna contracts follow strict Islamic laws. They avoid interest, which is not allowed in Islam. The contract ensures fairness between buyer and seller. Both parties agree on price and delivery terms upfront. This transparency builds trust and meets religious requirements.
Flexibility In Manufacturing
Istisna allows customization of goods before production. Buyers can specify design, materials, and features. Sellers can adjust production to meet buyer needs. This flexibility supports various industries, from construction to manufacturing. It helps deliver products exactly as requested.
Risk Management
Istisna spreads risk fairly between parties. The seller takes responsibility for producing the item. The buyer pays in stages or after delivery. This arrangement reduces financial risk for both. It promotes smooth project completion and reduces disputes.
Common Uses In Finance
Istisna contracts play a vital role in Islamic finance. They provide flexible solutions for financing projects that require manufacturing or construction. These contracts allow parties to agree on the production and delivery of goods or assets at a future date. The contract suits many financial needs, especially in sectors requiring customized production. Below are common uses of Istisna contracts in finance.
Construction Financing
Istisna contracts are widely used in construction financing. Developers and clients agree on the building’s specifications and completion date. The financier funds the construction, and the builder delivers the finished project. This method ensures compliance with Islamic finance principles. It avoids interest by structuring payments as part of the contract price. This approach supports real estate and infrastructure development.
Manufacturing Projects
Manufacturers use Istisna contracts to finance product creation. Buyers place orders for specific goods to be made later. The contract defines the product details and delivery timeline. Payment terms are flexible and can be scheduled before or after delivery. This arrangement helps manufacturers manage cash flow and production costs. It also guarantees buyers receive goods that meet agreed standards.
Asset Development
Istisna is suitable for developing various assets beyond buildings and products. It can fund machinery, equipment, and vehicles. The contract supports custom designs and specifications. Developers receive funds to complete the asset, then deliver it to the buyer. This use of Istisna provides financial support without violating Islamic rules. It encourages growth in industries needing tailored assets.
Istisna Vs. Similar Contracts
Istisna shares similarities with other Islamic finance contracts, yet it holds unique features. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right contract for specific needs. Below, we compare Istisna with Salam, Ijarah, and Murabaha contracts.
Istisna And Salam
Both Istisna and Salam involve buying goods before they exist. Salam requires full payment upfront while Istisna allows deferred payment. Salam is mainly for agricultural products. Istisna suits manufactured or constructed goods. Delivery time in Istisna is flexible. Salam contracts must specify exact goods and delivery dates.
Istisna And Ijarah
Istisna is a contract for manufacturing or construction. Ijarah is a leasing contract for existing assets. In Istisna, ownership transfers after delivery. Ijarah lets the lessee use the asset for a period. Payment in Ijarah is rental-based. Istisna focuses on creating new goods, unlike Ijarah’s use of existing items.
Istisna And Murabaha
Murabaha involves selling goods at cost plus profit. The goods in Murabaha are ready for delivery. Istisna covers goods not yet produced. Payment in Murabaha is usually immediate or deferred. Istisna allows staged payments during production. Murabaha is simpler; Istisna suits complex manufacturing projects.
Challenges And Limitations
Istisna contracts hold an important place in Islamic finance. They allow financing for manufacturing or construction before the asset exists. Despite their benefits, these contracts face certain challenges and limitations. Understanding these issues helps in better application and management of Istisna agreements.
These challenges affect contract reliability, delivery, and market trust. Each area has unique concerns that need attention from all parties involved.
Contract Enforcement
Enforcing Istisna contracts can be difficult due to their complex nature. The contract involves future goods and multiple stages. Courts may find it hard to interpret terms clearly. Disputes often arise over quality, specifications, and delivery time. Lack of standardized regulations increases uncertainty. This situation can delay justice and raise costs for both parties.
Delivery Risks
Delivery risks are common in Istisna contracts. The asset is not ready at contract signing. Manufacturing or construction delays can occur. These delays affect project timelines and payments. Sometimes, the final product may not meet agreed specifications. Weather, supply chain issues, or labor problems can cause setbacks. Managing these risks requires clear terms and good communication.
Market Acceptance
Market acceptance of Istisna contracts varies widely. Some markets lack familiarity with this contract type. Businesses may prefer conventional financing methods. This limits growth and adoption of Istisna agreements. Awareness and education are needed to build trust. Islamic financial institutions must promote the benefits and clarity of Istisna. Greater acceptance will lead to more efficient use.
Istisna In Modern Islamic Finance
Istisna plays a key role in modern Islamic finance by supporting project and asset development. It allows financing for manufacturing goods or construction projects before they are completed. This contract helps businesses and banks work together, following Sharia principles without charging interest.
Financial institutions use Istisna to fund large projects with flexible payment terms. It suits industries like real estate, infrastructure, and manufacturing. The contract covers the entire process from order to delivery, ensuring clarity and trust between parties.
Role In Islamic Banking
Islamic banks use Istisna to finance custom-built assets. They provide funds to manufacturers or builders who deliver the product later. This helps customers avoid interest-based loans. Banks can structure payments in installments or a lump sum after delivery. Istisna ensures compliance with Islamic law and supports economic growth.
Product Offerings
Banks offer various Istisna products tailored to client needs. Common products include home construction finance, factory setup financing, and infrastructure projects. Each product defines delivery time, specifications, and payment schedule clearly. These offerings attract customers seeking Sharia-compliant solutions for long-term investments.
Case Studies
Several banks have successfully used Istisna contracts. For example, a bank in the Middle East financed a large housing project under Istisna. The contract allowed phased payments as construction progressed. Another case involved funding a factory setup in Southeast Asia, where the bank managed risks by closely monitoring the manufacturing process.
These examples show how Istisna helps meet real economic needs. It supports development without compromising Islamic principles. Many banks continue to expand Istisna use across different sectors worldwide.
Regulatory And Legal Aspects
The regulatory and legal framework of Istisna contracts is essential for ensuring their proper use in Islamic finance. These contracts must follow strict rules to meet both religious and legal requirements. Understanding these aspects helps maintain trust and transparency in financial transactions.
Different countries may have their own laws governing Istisna contracts, but they all aim to protect the rights of both buyers and sellers. Proper regulation also helps prevent disputes and promotes fair trade practices.
Shariah Guidelines
Shariah law guides the structure and execution of Istisna contracts. It requires that the contract clearly defines the manufacturing process and delivery time. Both parties must agree on the specifications and price before starting the work.
Interest (riba) is prohibited in these contracts. The contract must be free from uncertainty (gharar) and must involve actual work or manufacturing. Shariah boards review and approve these contracts to ensure compliance.
International Standards
Global Islamic finance bodies set standards for Istisna contracts. Organizations like AAOIFI provide rules and guidelines to harmonize practices worldwide. These standards help banks and financial institutions operate consistently across borders.
International standards cover contract terms, risk management, and ethical considerations. They support the growth of Islamic finance by building investor confidence and facilitating cross-border transactions.
Compliance Issues
Compliance with both Shariah and local laws is critical for Istisna contracts. Financial institutions must ensure contracts meet all legal requirements to avoid penalties. Non-compliance can lead to contract invalidation or financial losses.
Regular audits and Shariah reviews help identify and resolve compliance issues. Training staff in Islamic finance principles also reduces risks. Clear documentation and transparency are key to maintaining compliance.
Future Trends
The Istisna contract holds a vital place in Islamic finance. It supports manufacturing and construction projects. As markets evolve, Istisna adapts to modern needs. Future trends show how this contract stays relevant and useful.
These trends focus on technology, market expansion, and new uses. Each area helps Istisna meet the demands of today’s economy. Understanding these trends guides investors and businesses alike.
Technological Integration
Technology is changing how Istisna contracts work. Digital platforms make contract management faster and clearer. Blockchain ensures transparency and reduces fraud risks. Smart contracts automate payments upon project milestones. These tools build trust between buyers and sellers. They also lower costs and improve efficiency.
Market Growth
Islamic finance is growing worldwide, especially in construction and manufacturing. More companies choose Istisna for project financing. New regions adopt Sharia-compliant contracts for infrastructure development. This growth drives demand for skilled professionals and legal experts. Rising awareness boosts Istisna’s acceptance in global markets.
Innovative Applications
Istisna is no longer limited to traditional projects. It now supports renewable energy and technology products. Custom-made goods and large-scale developments benefit from this contract. Financial institutions create hybrid models combining Istisna with other contracts. These innovations expand the contract’s usefulness and appeal.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Istisna In Islamic Finance?
Istisna in Islamic finance is a contract to manufacture or construct an asset, paid in advance or installments, following Sharia principles. It supports custom orders before the asset exists, avoiding interest and ensuring ethical financing in project development and manufacturing.
What Is The Meaning Of Istasna In Islam?
Istisna in Islam is a contract where a buyer requests manufacturing or construction of an asset before its existence. It complies with Sharia by avoiding interest and involves payment upon completion or in installments. This contract supports Islamic finance by enabling asset creation through ethical agreements.
What Is The Difference Between Istisna And Ijarah?
Istisna is a contract to manufacture and deliver a product later. Ijarah is a lease contract for using an existing asset. Istisna involves manufacturing; Ijarah involves renting.
What Are The Three Contracts Applied In Islamic Finance?
The three main contracts in Islamic finance are Murabaha, Salam, and Istisna. They ensure Sharia compliance by avoiding interest and promoting asset-backed transactions.
Conclusion
Istisna contract plays a key role in Islamic finance today. It allows buying goods before they exist, supporting manufacturing and construction. This contract follows Sharia rules, avoiding interest and unfairness. Many businesses use Istisna to fund projects with clear terms and timelines.
Understanding Istisna helps individuals and companies make informed financial decisions. It ensures ethical and practical solutions for asset creation. This contract reflects Islamic finance’s goal of fairness and transparency. Exploring Istisna opens doors to new opportunities in compliant finance.