Are you looking for a financing solution that aligns with your values and offers a true partnership in business? Musharakah financing might be exactly what you need.
It’s a unique approach where you and your financier become partners, sharing both the risks and rewards. Imagine having a financial arrangement that doesn’t just treat you like a borrower, but as an equal collaborator in success. Whether you’re starting a new venture or expanding an existing one, understanding Musharakah can open doors to smarter, more ethical funding options.
Keep reading to discover how this Islamic finance model works, its benefits, and how it can transform the way you grow your business or invest in property.
Basics Of Musharakah
Musharakah financing is a unique Islamic finance method. It is based on partnership and shared goals. This method involves cooperation between parties to fund a business or project. Each partner contributes capital and shares the results. Understanding the basics of Musharakah is key to grasping its benefits and rules.
Joint Venture Concept
Musharakah works like a joint venture. Two or more parties come together to invest money. They combine resources to start or run a business. Each partner owns a share of the venture. The share depends on the amount of capital they provide. This cooperation helps spread the risk and rewards.
Profit And Loss Sharing
In Musharakah, profits are shared based on a pre-agreed ratio. This ratio can differ from the capital share. Losses, however, are shared strictly according to the capital contributed. This rule ensures fairness and transparency. It encourages partners to work hard and manage the business well.
Sharia Compliance
Musharakah financing follows strict Sharia law rules. It prohibits earning interest (riba). The focus is on genuine trade and investment activities. Contracts must be clear and agreed upon by all partners. This compliance makes Musharakah a preferred option for Muslims seeking ethical finance.
Types Of Musharakah
Musharakah financing involves partners pooling their capital to share profits and losses. This partnership model supports various business ventures and investments. Understanding its types helps in choosing the right Musharakah structure for specific needs.
Each type of Musharakah offers a unique way to manage ownership and profit sharing. The choice depends on the project’s duration and the partners’ roles.
Permanent Musharakah
Permanent Musharakah is a long-term partnership. Partners contribute capital and share profits or losses continuously. No partner is expected to withdraw their share. This type suits ongoing businesses or joint ventures. All partners have equal rights in management decisions.
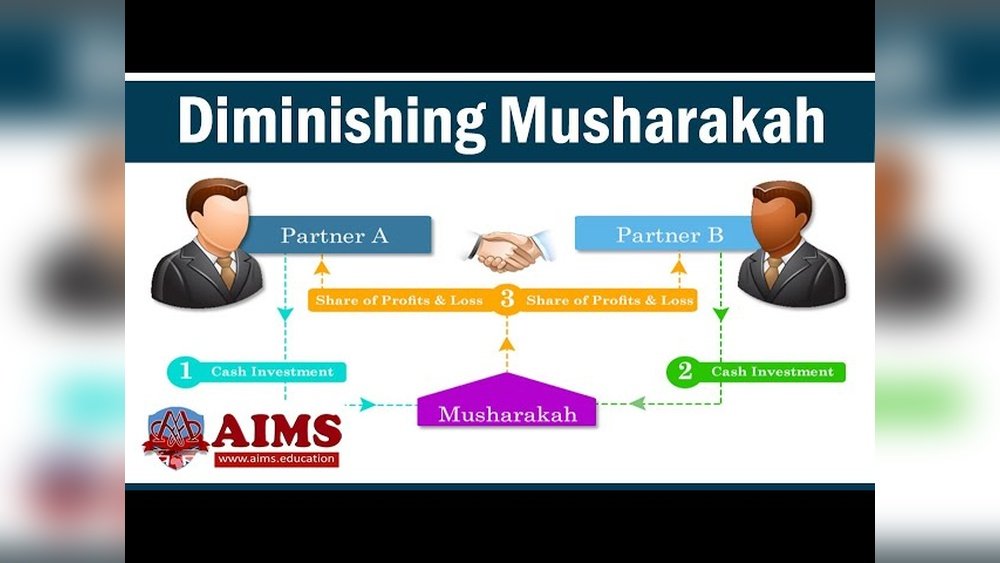
Diminishing Musharakah
Diminishing Musharakah involves one partner gradually buying the other’s share. It starts as a joint ownership and ends with sole ownership. This model is popular in property financing. The buyer pays rent and installments to acquire full ownership over time.
Musharakah Mutanaqisah
Musharakah Mutanaqisah means “declining partnership” in Arabic. It is similar to diminishing Musharakah. The buyer’s share increases while the financier’s share decreases. Both parties share profits according to their ownership. The buyer eventually owns the asset fully after all payments.
Musharakah Vs Other Islamic Financing
Musharakah financing stands out among Islamic finance methods. It involves a partnership where all parties share capital, profits, and losses. Understanding how Musharakah compares to other Islamic financing options helps in choosing the right solution.
This section covers key differences and when Musharakah works best.
Comparison With Murabaha
Murabaha is a cost-plus financing method. The bank buys an asset and sells it to the client at a marked-up price. The client pays in installments. Profit is fixed and agreed upon in advance.
Musharakah differs as both partners invest capital and share profits and losses. It promotes risk-sharing rather than fixed returns. Musharakah suits long-term projects, unlike Murabaha’s short-term nature.
Differences From Ijara
Ijara is a leasing contract where the bank buys an asset and leases it to the client. The client pays rent but does not own the asset during the lease. Ownership may transfer after the lease ends.
Musharakah involves joint ownership from the start. Both parties have rights and responsibilities towards the asset. Profit and loss sharing depends on the actual business performance, unlike fixed rent in Ijara.
When To Choose Musharakah
Choose Musharakah for ventures needing shared investment and risk. It fits startups and joint business projects. Both partners participate in decisions and share outcomes.
This method benefits those who want active involvement and flexible profit distribution. Musharakah works well when trust and cooperation exist between partners.
Applications Of Musharakah
Musharakah financing offers a flexible way to share investment risks and rewards. It involves partners contributing capital and sharing profits and losses equally or as agreed. This model suits various financial needs and projects.
Below are some common applications of Musharakah financing.
Business Partnerships
Musharakah is ideal for business partnerships. Partners pool their money to start or grow a business. Each partner shares in profits and losses based on their share. This encourages cooperation and fair risk sharing. It helps small and medium businesses access funds without interest.
Home Financing
Musharakah is used in home financing through shared ownership. The bank and buyer jointly purchase the property. Over time, the buyer gradually buys the bank’s share. Monthly payments include rent and purchase installments. This method suits those avoiding conventional loans with interest.
Large Project Funding
Large projects need significant capital and risk sharing. Musharakah allows investors to come together and fund such projects. They share profits and losses based on their investment. It supports infrastructure, real estate, and industrial projects. This financing is transparent and follows Islamic principles.
Benefits Of Musharakah
Musharakah financing offers a unique approach to business partnerships. It creates a fair and transparent way to share both profits and risks. This system supports cooperation and trust between partners. Many find Musharakah beneficial for ethical and balanced financial growth.
Profit Sharing Advantages
Partners share profits based on agreed ratios. This method motivates all parties to work hard. Profit sharing links returns directly to business success. It avoids fixed interest payments, making it flexible. Everyone benefits from the company’s growth.
Risk Sharing Mechanism
Risks are divided among partners according to their investment. This reduces the burden on a single party. Losses are shared fairly, reflecting real business outcomes. It creates a balanced and stable financial environment. Risk sharing encourages cautious and wise decisions.
Encouraging Ethical Investments
Musharakah promotes investments that follow Islamic law. It forbids interest and unethical activities. Partners choose projects that benefit society and economy. This builds trust and long-term relationships. Ethical investments support sustainable and responsible growth.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Challenges And Risks
Musharakah financing offers a partnership-based approach to funding projects. It shares profits and losses among partners. Despite its benefits, this model faces several challenges and risks. Understanding these issues helps partners manage their ventures better.
Capital Contribution Issues
Partners must contribute capital fairly. Unequal or delayed contributions can create disputes. Sometimes, one partner may provide more funds but expect a larger share. This situation can harm trust and cooperation.
Capital valuation can be tricky. Partners may disagree on how to value non-cash assets. Clear agreements on contribution terms are essential to avoid conflicts.
Profit Distribution Conflicts
Profit sharing depends on agreed ratios. Disputes often arise if profits do not meet expectations. Some partners may feel they deserve more than their share. This can lead to tension and business disruption.
Loss sharing also causes challenges. Partners must accept losses proportionate to contributions. Some may resist sharing losses equally, causing friction within the partnership.
Regulatory Considerations
Musharakah financing must follow Islamic law and local regulations. Different countries have varying rules about Islamic finance. Compliance can be complex and costly.
Regulators may require detailed reporting and transparency. Failure to meet these rules risks penalties or legal issues. Partners must stay informed about changing regulations to remain compliant.
Steps To Establish Musharakah
Establishing a Musharakah partnership involves clear steps. Each step ensures fairness and compliance with Islamic finance principles. Understanding these steps helps partners build trust and work smoothly together. The process starts with choosing the right partner. Then, partners structure the agreement carefully. Finally, they decide how to share profits and losses.
Partner Selection
Choosing the right partner is the first step. Both parties must agree on the business goals. Trust and transparency are essential in this stage. Partners should have compatible values and skills. Capital contribution from each partner must be clear. This creates a strong foundation for the partnership.
Agreement Structuring
The partnership agreement defines each partner’s role and share. It explains how the business will operate. Clear terms reduce misunderstandings later. The agreement should follow Islamic law rules. It must outline capital investment and management duties. Legal advice can help make the agreement solid.
Profit And Loss Agreement
Profit and loss sharing is the core of Musharakah. Partners agree on how to divide profits fairly. Losses are shared according to capital contribution. This rule ensures no party bears unfair risk. The agreement must be clear and accepted by all. This maintains balance and trust in the partnership.
Musharakah In Austin, Texas
Musharakah financing is gaining attention in Austin, Texas. It offers a partnership approach to funding. This model aligns with Islamic finance principles. Both partners share profits and losses. Austin’s diverse economy welcomes such ethical finance options. Local businesses and investors explore Musharakah for growth and collaboration.
Market Opportunities
Austin’s economy is vibrant and growing fast. Small businesses and startups thrive here. Musharakah financing fits well with this growth. It supports businesses needing shared investment and risk. The tech sector and real estate market show strong demand. Muslim entrepreneurs find Musharakah a suitable funding method. This creates a niche yet expanding market.
Local Regulatory Environment
Austin follows Texas state laws for business financing. Regulations allow flexible partnership agreements like Musharakah. Authorities require transparency and fair profit sharing. Islamic finance firms comply with both Sharia and local rules. Licensing for Islamic financial institutions is available. This legal clarity helps Musharakah partnerships succeed. It encourages more investors and entrepreneurs to join.
Success Stories
Several Austin businesses have benefited from Musharakah financing. A tech startup raised capital through a Musharakah partnership. Both parties shared risks and profits fairly. Another success involved a real estate project funded this way. These cases show Musharakah’s practical value. They inspire others to consider this ethical financing option. Trust and cooperation drive these positive outcomes.
Future Trends
The future of Musharakah financing shows strong growth and new possibilities. This model adapts to changing markets and technology. It offers flexible options for investors and entrepreneurs alike.
Emerging trends focus on improving efficiency, expanding reach, and creating better contract models. These changes aim to meet the needs of a wider audience.
Technological Integration
Technology plays a key role in Musharakah’s future. Digital platforms simplify the partnership process. They allow quick and transparent communication between partners.
Blockchain can record contracts securely and reduce risks. Smart contracts automate profit and loss sharing. This reduces disputes and speeds up transactions.
Expansion In Western Markets
Musharakah financing is gaining interest outside traditional Islamic countries. Western markets show growing demand for ethical and shared-risk financing. This model fits well with socially responsible investment ideas.
More banks and financial institutions in the West are exploring Musharakah products. This expansion increases opportunities for cross-border partnerships and diverse funding sources.
Innovations In Contract Models
Contract models in Musharakah are evolving to become more flexible. New agreements focus on clearer profit-sharing rules and loss responsibilities. This reduces misunderstandings and builds trust.
Hybrid models combine Musharakah with other Islamic finance tools. This innovation helps tailor solutions for various business needs and risk levels. It enhances the appeal of Musharakah to different sectors.

Credit: cbonds.com

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Meaning Of Musharakah Financing?
Musharakah financing is an Islamic partnership where parties jointly invest capital and share profits and losses based on their contributions.
What Is An Example Of Musharakah?
An example of Musharakah is two partners investing capital to start a business, sharing profits and losses equally.
What Are The Three Types Of Islamic Mortgage?
The three types of Islamic mortgage are Ijara (leasing), Diminishing Musharaka (shared ownership), and Murabaha (cost-plus financing). Each complies with Sharia by avoiding interest and sharing profit or usage rights.
What Is The Difference Between Murabaha And Musharakah?
Murabaha involves a seller-financier selling goods at a profit, with fixed repayment. Musharakah is a partnership sharing profits and losses equally. Murabaha suits short-term financing, while Musharakah supports long-term joint ventures.
Conclusion
Musharakah financing offers a fair way to share profits and risks. It encourages cooperation between partners in business ventures. Both parties invest capital and work together for success. This approach follows Islamic principles, avoiding interest and promoting shared responsibility. It suits those seeking ethical and transparent financing methods.
Understanding Musharakah helps make better financial decisions in Islamic banking. Consider it as a practical option for joint investments and projects. Clear terms and mutual trust remain essential for Musharakah’s success. Explore this method for balanced and responsible financing solutions.