Are you looking for a smart way to grow your business or invest your money with a trusted partner? Understanding the Musharakah Joint Venture can open new doors for you.
This unique partnership lets you and your partner combine resources, share profits, and face risks together—making your business journey more balanced and fair. Imagine having a partner who is as invested in your success as you are, sharing both rewards and challenges.
You’ll discover exactly how Musharakah works, why it stands out from other business partnerships, and how it can benefit your financial goals. Keep reading to unlock the secrets of this powerful joint venture model and take your business to the next level.
Musharakah Basics
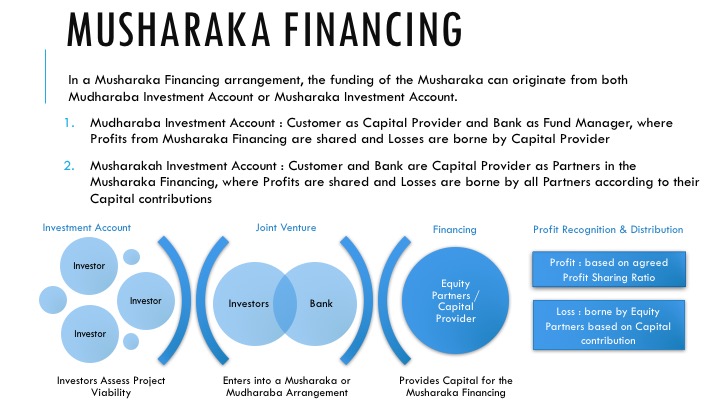
Musharakah is a type of partnership used in Islamic finance. It allows two or more parties to work together in a business venture. Each partner contributes capital or assets to the project. The goal is to share profits and losses fairly. This joint venture follows clear rules to ensure fairness and transparency. Understanding Musharakah basics helps businesses and investors choose the right partnership model.
Key Principles
Musharakah is based on trust and mutual agreement. All partners must contribute capital or assets. Each partner’s share is clearly defined at the start. Management can be shared or assigned to specific partners. Transparency in all dealings is essential. The partnership must avoid interest (riba) to comply with Islamic law.
Types Of Musharakah
There are two main types of Musharakah. First is Permanent Musharakah, where the partnership lasts indefinitely. Partners share profits and losses as agreed. Second is Diminishing Musharakah. One partner gradually buys out the other’s share. This type is often used in home financing. Both types focus on fairness and clear terms.
Profit And Loss Sharing
Profit sharing depends on the agreement among partners. It may not match the capital contribution ratio. Losses must be shared according to each partner’s investment. This rule protects all partners from unfair burden. Partners are responsible for managing risks together. Clear profit and loss rules ensure trust and cooperation.
Credit: islamicbankers.center
Musharakah Vs Mudarabah
Musharakah and Mudarabah are two common types of Islamic finance partnerships. Both follow Sharia principles but differ in structure and roles. Understanding these differences helps businesses choose the right model for their needs.
Each model defines how capital is contributed, who manages the business, and how profits and losses are shared. These factors affect partnership dynamics and risk distribution.
Capital Contributions
In Musharakah, all partners contribute capital. This capital can be money, property, or other assets. Each partner’s share depends on their contribution.
In Mudarabah, only one party provides capital. The other partner offers expertise and manages the business. The financier does not take part in daily operations.
Management Roles
Musharakah allows all partners to manage the business. Each partner can participate in decisions and operations.
Mudarabah gives management control to the entrepreneur. The financier stays passive and does not interfere with business decisions.
Loss And Profit Distribution
Profits in Musharakah are shared based on the partners’ capital shares or as agreed. Losses are always shared in proportion to capital contributions.
In Mudarabah, profits are shared according to a pre-agreed ratio. Losses are borne only by the financier. The entrepreneur loses time and effort but no capital.
Asset Ownership
All partners jointly own the assets in Musharakah. The ownership corresponds to the amount of capital each partner invests.
In Mudarabah, the financier owns the capital assets. The entrepreneur owns no part of the capital but manages its use.
Setting Up A Musharakah Venture
Setting up a Musharakah joint venture requires clear planning and agreement. This Islamic partnership involves shared investment and profit distribution. Each partner brings value and shares risk. The process begins with selecting the right partners. Next comes drafting a solid agreement. Finally, partners must agree on contribution ratios.
Choosing Partners
Partners must trust each other and share common goals. They should have compatible skills and resources. Choose partners who understand Musharakah principles. This ensures smooth cooperation and fair profit sharing. A good partner adds value beyond money.
Drafting The Agreement
The agreement defines roles, rights, and responsibilities of each partner. It clarifies profit and loss distribution methods. Include terms for managing the venture and resolving disputes. Use clear, simple language to avoid confusion. A well-drafted contract protects everyone’s interests.
Determining Contribution Ratios
Contribution ratios decide how much each partner invests. This can be money, assets, or effort. Profit and loss shares depend on these ratios. Agree on fair ratios before starting the venture. Accurate ratios ensure transparent and just sharing of results.
Operational Aspects
The operational aspects of a Musharakah joint venture focus on how partners work together daily. These aspects shape the success and smooth running of the partnership. Understanding management, decision-making, and dispute handling is essential for all partners.
Management Participation
In Musharakah, all partners can take part in managing the business. Each partner has a right to contribute ideas and oversee operations. This shared management helps balance responsibilities and uses each partner’s skills. Partners must agree on their roles clearly to avoid confusion.
Decision-making Processes
Decisions in Musharakah are made jointly by all partners. They discuss and agree on important matters before taking action. Voting may be used when partners disagree. The agreed method should be fair and clear to all partners from the start. This keeps the partnership stable and transparent.
Handling Disputes
Disputes can arise in any business partnership. Musharakah partners should plan how to resolve conflicts early. They may use negotiation or mediation to find solutions. Clear communication helps prevent small issues from growing. Having a written agreement on dispute handling is very helpful.
Financial Management
Financial management is crucial in a Musharakah joint venture. It ensures clear handling of money, profits, and losses. Proper management builds trust among partners. It keeps the business stable and fair for everyone involved.
Partners must agree on how to share profits and cover losses. Accurate record-keeping and transparent accounting help avoid disputes. Good financial practices support smooth operations and long-term success.
Profit Allocation Methods
Profit sharing in Musharakah depends on the agreement between partners. Usually, profits are divided in proportion to each partner’s investment. Partners can also agree on different profit ratios if all consent. Clear profit allocation prevents misunderstandings and keeps relations strong.
Loss Sharing Mechanisms
Losses in a Musharakah joint venture are shared according to capital contribution. Each partner bears losses in the same ratio as their investment. This rule ensures fairness and aligns risks with rewards. Partners must accept this principle before starting the venture.
Accounting Practices
Accurate accounting is vital for Musharakah financial management. All transactions must be recorded clearly and timely. Partners should maintain joint books or use shared accounting software. Transparent accounting helps track profits, losses, and capital changes. It also supports accountability and trust among partners.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Legal And Regulatory Considerations
Entering a Musharakah joint venture requires clear understanding of legal and regulatory aspects. This ensures smooth operation and protects all parties involved. Different regions may have specific rules to follow. Proper attention to these rules reduces risks and builds trust.
Compliance With Shariah
Musharakah ventures must follow Islamic law, or Shariah. This means contracts must avoid interest (riba) and unfair terms. Profit and loss sharing must be clear and fair. A Shariah board or advisor often reviews agreements. This helps ensure the partnership meets religious and ethical standards.
Local Business Laws
Local laws govern business formation, taxes, and permits. Partners must register the joint venture according to local rules. Compliance with labor, tax, and commercial laws is essential. Ignoring these laws can cause fines or closure. Understanding local laws helps avoid legal problems and delays.
Contract Enforcement
Clear contracts are key for resolving disputes. The agreement should state roles, profit shares, and exit terms. Courts or arbitration bodies enforce these contracts. Choosing the right legal venue matters for smooth enforcement. Well-drafted contracts protect all partners from conflicts.
Benefits Of Musharakah Partnerships
Musharakah partnerships offer a unique way for businesses to grow together. They build trust by sharing both profits and losses. This approach encourages fairness and cooperation among partners. The benefits extend beyond money, impacting skills and resources.
Shared Risks And Rewards
In Musharakah, all partners share the risks involved. No single partner bears the entire loss. Profits are also divided based on each partner’s contribution. This balance creates fairness and motivates everyone to work hard. The shared responsibility reduces fear of failure. It helps build stronger, long-lasting partnerships.
Access To Capital
Musharakah allows businesses to pool their funds. This combined capital supports larger projects and expansions. Partners with limited funds can still join in. Those with excess capital can invest effectively. The partnership makes funding easier to obtain. It reduces dependency on loans and interest payments.
Enhanced Business Expertise
Each partner brings unique skills and knowledge. Combining these strengths improves business decisions. Partners can solve problems faster and better. This teamwork leads to innovation and growth. The partnership creates a learning environment for everyone. It increases the chance of business success.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Common Challenges
Musharakah joint ventures face several common challenges that partners must handle carefully. These challenges can affect the success and harmony of the partnership. Understanding these issues helps in creating stronger agreements and smoother cooperation.
Capital Imbalance
Capital imbalance occurs when partners contribute unequal amounts. This difference can cause tension about control and decision-making. Partners with larger investments may feel they deserve more influence. Smaller investors might fear their interests are overlooked. Clear terms about capital and roles prevent misunderstandings.
Management Conflicts
Management conflicts arise when partners disagree on running the business. Different ideas about strategies and daily operations create friction. Lack of clear leadership or decision rules worsens the problem. Defining roles and responsibilities early reduces disputes and keeps the venture stable.
Profit Disputes
Profit disputes happen when partners disagree on sharing earnings. Differences in expectations or unclear profit-sharing terms can cause conflicts. Partners may argue about reinvestment or distribution of profits. Agreeing on transparent methods for calculating and sharing profits is essential.
Successful Musharakah Examples
Musharakah joint ventures create opportunities for shared growth and profit. Successful examples show how partners combine resources and skills. Both small and large projects benefit from this Islamic partnership model. It encourages fairness by sharing profits and losses according to contributions.
Below are examples across different sectors where Musharakah partnerships have thrived. Each highlights unique ways partners collaborate for mutual success.
Small Business Ventures
Small businesses use Musharakah to pool capital and expertise. For example, two friends start a café together. One invests money, the other manages daily operations. They share profits based on their agreement. This reduces financial risk and builds trust. Many local shops and service providers use this model.
Real Estate Projects
Real estate developers often form Musharakah partnerships. One partner provides land, another provides construction funds. They share rental income or sales profits fairly. This method avoids debt and interest issues. It also helps complete projects faster with joint effort. Large apartment complexes and commercial buildings benefit from Musharakah.
Technology Startups
Tech startups gain from Musharakah by combining innovation with capital. An investor funds a new app, while the founder offers technical skills. They agree on profit sharing and risk sharing. This encourages long-term commitment from both sides. Many new software and hardware companies grow this way.
Tips For Profitable Musharakah
Profitability in a Musharakah joint venture depends on clear planning and strong collaboration. Partners need to focus on important practices that keep the venture successful and fair. These tips help avoid conflicts and ensure smooth operations in the partnership.
Clear Agreement Terms
Start with a detailed agreement that explains each partner’s role. Define capital contributions, profit shares, and loss responsibilities clearly. Set rules for decision-making and conflict resolution. A clear contract prevents misunderstandings and builds trust.
Regular Communication
Keep open and honest communication among partners. Schedule regular meetings to discuss progress and challenges. Share financial updates and business developments openly. Good communication helps catch problems early and strengthens teamwork.
Flexible Profit Sharing
Agree on profit-sharing terms that can adapt to business changes. Consider revising profit ratios if contributions or market conditions shift. Flexibility motivates partners to stay committed and supports long-term growth. Fair sharing keeps all partners engaged and satisfied.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Example Of Musharakah?
An example of musharakah is two partners starting a business together, sharing capital, profits, and losses based on their contributions.
How Does Musharaka Work?
Musharaka is a joint partnership where all partners contribute capital and share profits and losses proportionally. Partners jointly manage the business and share risks based on their investment. This Islamic finance model promotes equitable participation and compliance with Sharia principles.
What Is The Difference Between Mudarabah And Musharakah?
Musharakah involves all partners contributing capital and sharing profits and losses. Mudarabah has one financier providing capital, and the entrepreneur managing without financial loss.
What Are The 4 Categories Of Shariah Contracts?
The four categories of Shariah contracts are Sale (Bai), Partnership (Musharakah), Trust Financing (Mudarabah), and Lease (Ijarah). Each defines specific rights and obligations under Islamic law.
Conclusion
Musharakah joint ventures offer a fair way to share profits and losses. Partners invest capital and work together closely. This partnership encourages trust and shared responsibility. It suits businesses wanting equal participation and risk sharing. Understanding Musharakah helps in making smart, ethical financial decisions.
Always review terms carefully before entering any Musharakah agreement. This approach supports growth while respecting Islamic finance principles. Musharakah remains a valuable option for cooperative business ventures worldwide.
