If you want to explore a unique way of investing that aligns with ethical and religious principles, understanding Sukuk bonds is essential. Unlike traditional bonds, Sukuk bonds offer you a chance to own a share in real assets while earning returns based on their actual performance.
But how exactly are these bonds structured? And why do they stand out in the world of finance? This article breaks down the Sukuk bonds structure in simple terms, guiding you step-by-step through the key features that make them both compliant with Islamic law and appealing to a wide range of investors.
Keep reading to discover how Sukuk can fit into your investment strategy and why they are gaining popularity worldwide.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Sukuk Basics
Sukuk are financial certificates used in Islamic finance. They provide an alternative to conventional bonds. Sukuk comply with Islamic law, known as Shariah. These certificates represent ownership in assets, not debt. This unique structure makes sukuk different from regular bonds.
Investors in sukuk share in the profits and risks of the underlying asset. This approach aligns with ethical and religious principles. Understanding the basics of sukuk helps grasp their role in global finance.
Shariah Principles
Sukuk must follow Shariah rules strictly. These rules forbid earning interest, called riba. Instead, profits come from actual asset performance. Speculation and uncertainty, known as gharar, are also avoided. Investments must be ethical and socially responsible. Every sukuk structure is reviewed by a Shariah board to ensure compliance.
Difference From Conventional Bonds
Conventional bonds involve lending money for fixed interest payments. Sukuk represent ownership in tangible assets. Investors earn returns from asset profits, not interest. The risk is shared between issuer and investor. This prevents unfair gains and losses. Sukuk also avoid investments in forbidden industries like alcohol or gambling.
Asset Ownership Concept
Sukuk holders have partial ownership of an asset or project. This ownership gives them rights to the asset’s income. Assets can include real estate, infrastructure, or equipment. The asset must be clearly identified and valued. Ownership links the sukuk directly to the asset’s performance. This ensures transparency and fairness in returns.
Credit: www.whitecase.com
Core Sukuk Structures
Sukuk bonds offer a unique way to invest while following Islamic law. These bonds are based on real assets and avoid interest payments. Instead, they give investors a share in the asset’s profits. Core Sukuk structures define how these bonds are created and managed. Each structure uses different contracts and methods to ensure compliance with Sharia principles.
Understanding the main types helps investors choose the right Sukuk. The core structures include Ijarah, Murabaha, Mudarabah, and Musharakah. Each has its own features and benefits. They all share one goal: linking the investment to real assets and shared risk.
Ijarah Sukuk
Ijarah Sukuk is based on leasing. The issuer buys an asset and leases it to a user. Investors get rent payments from the lease. This rent is the return on their investment. The asset stays owned by the Sukuk holders during the lease. This structure is simple and popular for real estate and equipment financing.
Murabaha Sukuk
Murabaha Sukuk involves buying and selling goods. The issuer buys an asset and sells it to the investor at a fixed profit. The investor pays in installments over time. This profit replaces interest payments. Murabaha Sukuk is common for trade financing and short-term funding needs.
Mudarabah Sukuk
Mudarabah Sukuk works like a partnership. Investors provide capital to a business manager. The manager runs the project and shares profits with investors. Losses are borne only by investors unless caused by manager’s negligence. This structure encourages profit-sharing and risk-taking under Sharia rules.
Musharakah Sukuk
Musharakah Sukuk is a joint venture. Investors and the issuer both contribute funds to a project. They share profits and losses based on their shares. This structure promotes cooperation and shared responsibility. It suits long-term projects like infrastructure and development.
How Sukuk Work
Sukuk bonds follow a unique structure based on Islamic finance rules. They provide investors a share in an ownership of assets, not just a loan. Understanding how sukuk work helps explain their growing popularity worldwide.
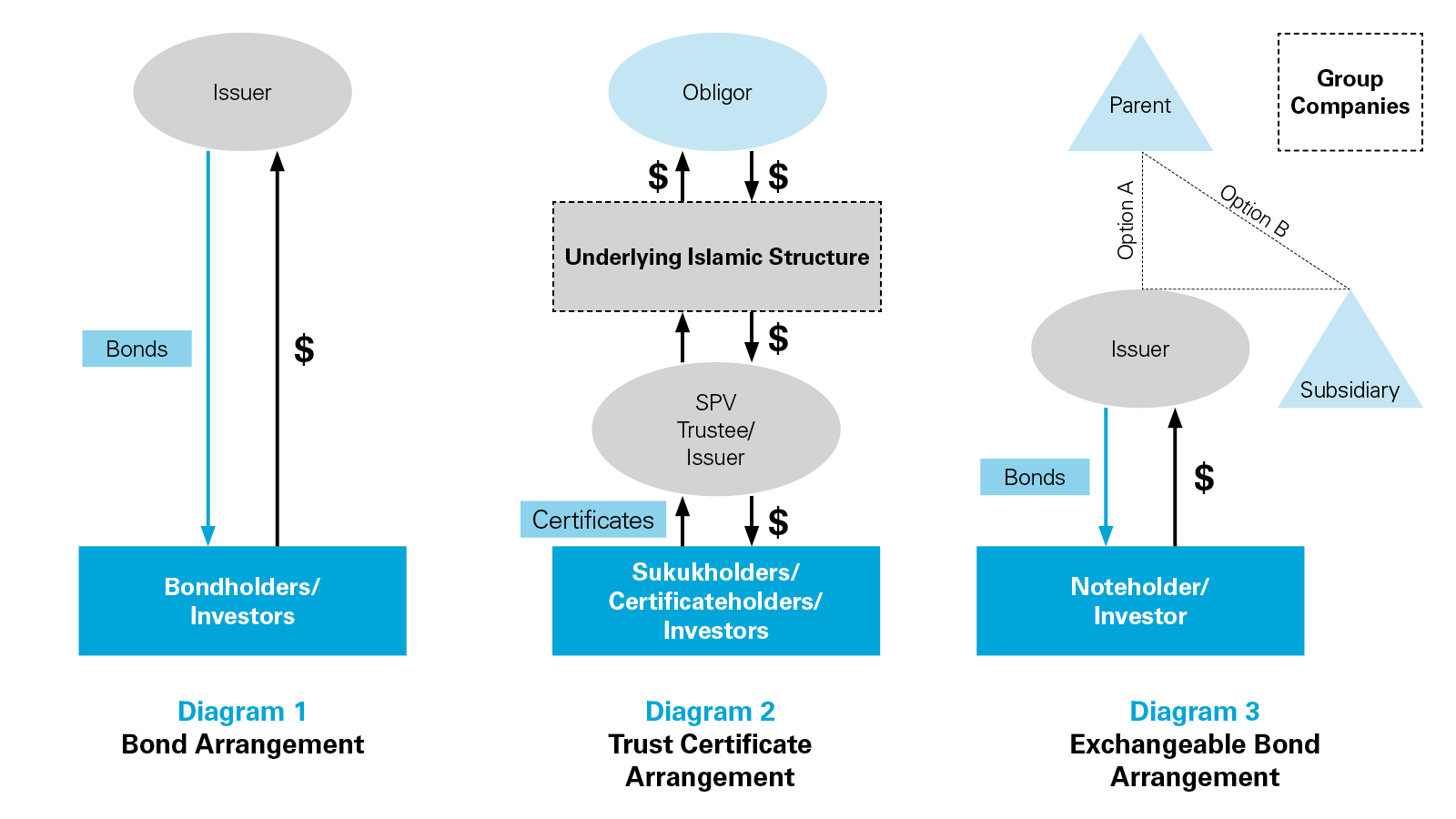
The process starts with creating trust certificates. These certificates represent ownership in tangible assets or projects. Investors receive returns linked to the asset’s performance, not fixed interest payments. This structure aligns with Sharia principles, avoiding forbidden interest (riba).
Trust Certificates
Trust certificates are the foundation of sukuk. They prove investors own part of an asset or project. The issuer sets up a trust to hold the asset. Investors buy certificates from this trust. This setup ensures clear ownership and transparency.
The certificates are tradable, providing liquidity in the market. Each certificate entitles holders to a share of income from the asset. This could be rent, profits, or other earnings generated by the asset.
Profit And Risk Sharing
Sukuk investors share both profit and risk from the underlying asset. Returns depend on the asset’s actual performance. If the asset makes profit, investors receive a share. If it loses value, investors share the loss.
This profit and risk sharing contrasts with conventional bonds, which offer fixed interest regardless of asset performance. It encourages fairness and transparency. The risk-sharing nature makes sukuk attractive to ethical investors.
Underlying Asset Role
The underlying asset is central to sukuk structure. It must be tangible and Sharia-compliant. Common assets include real estate, infrastructure, or business ventures. The asset provides the income source for the sukuk holders.
Ownership of the asset by the trust supports the sukuk’s legitimacy. Returns to investors depend on this asset’s income or sale. This link to real assets reduces speculation and aligns with Islamic finance values.
Shariah Compliance Process
The Shariah compliance process is essential in structuring sukuk bonds. It ensures that every step aligns with Islamic law. This process protects investors by confirming that investments are ethical and free from interest (riba). The process involves detailed reviews and approvals by qualified experts. It guarantees that sukuk bonds remain asset-backed and follow Shariah principles strictly.
Role Of Sharia Boards
Sharia boards consist of Islamic scholars and experts. They review all sukuk documents and contracts. Their role is to ensure compliance with Islamic law. These boards provide guidance on permissible financial activities. They also monitor sukuk issuance and ongoing operations. Their approval is mandatory before any sukuk can be marketed or sold. This helps build trust among Muslim investors.
Approval Mechanisms
Approval mechanisms involve several steps and checks. Each sukuk structure is examined against Shariah rules. The process includes reviewing contracts, underlying assets, and profit-sharing methods. The Sharia board issues a formal certification called a fatwa if all conditions are met. This fatwa certifies the sukuk as Shariah-compliant. Without this certification, sukuk cannot proceed to the market. Approval also involves continuous oversight during the sukuk’s life.
Ensuring Asset-backed Investments
Asset backing is a core principle of sukuk bonds. The investment must represent ownership in tangible assets. These assets generate income, such as rent or profits from business operations. Sharia boards verify that the assets are lawful and properly valued. They ensure the sukuk is not merely a debt instrument. This structure avoids interest payments and links returns to asset performance. It provides transparency and reduces speculative risks for investors.
Benefits Of Sukuk
Sukuk bonds offer unique benefits that appeal to many investors. They provide a way to invest while following Islamic finance rules. These benefits make sukuk a popular choice for diverse portfolios. Understanding these advantages helps explain why sukuk gain global interest.
Halal Investment Opportunity
Sukuk is a halal investment. It follows Islamic laws that forbid earning interest. Instead, investors gain shares in real assets. This structure makes sukuk acceptable to Muslim investors. It allows them to grow wealth without breaking religious rules.
Diversification Advantages
Sukuk helps diversify investment portfolios. It offers exposure to different asset classes. These include real estate, infrastructure, and business ventures. Diversification lowers overall investment risk. It balances portfolios and can improve returns.
Attracting Ethical Investors
Ethical investors seek responsible investment options. Sukuk aligns with ethical and social values. It promotes transparency and asset backing. This attracts investors focused on fairness and social impact. Sukuk supports sustainable and ethical finance practices.
Challenges In Sukuk Market
The sukuk market faces several challenges that affect its growth and acceptance worldwide. These challenges arise from structural, financial, and regulatory factors. Understanding these obstacles is key to grasping the dynamics of sukuk bonds.
The market struggles with issues that limit investor confidence and market efficiency. These difficulties also slow down the development of new sukuk products and markets.
Credit Rating Issues
Credit ratings play a vital role in the sukuk market. Many issuers face difficulties obtaining strong credit ratings. This problem limits investor trust and reduces demand. Rating agencies often lack clear criteria for sukuk products. This uncertainty causes inconsistent ratings across markets. Lower credit ratings increase borrowing costs for issuers. It also restricts access for smaller or less-known companies.
Market Liquidity
The sukuk market suffers from low liquidity. Few investors trade sukuk regularly, which makes selling difficult. Limited secondary market activity discourages new investors. This situation raises the risk for holders who want to exit early. The small size of many sukuk issues also contributes to poor liquidity. Without enough buyers and sellers, price discovery becomes inefficient. This problem prevents sukuk from competing well with conventional bonds.
Regulatory Hurdles
Regulatory differences between countries create challenges for sukuk issuance. Diverse legal frameworks affect the structuring and approval of sukuk deals. Some jurisdictions lack clear rules for asset ownership and transfer. These gaps raise legal risks and slow down issuance. Tax treatment of sukuk varies widely and can reduce returns. Regulatory uncertainty also deters international investors. Harmonizing regulations remains a major goal for the global sukuk market.
Global Sukuk Trends
The global sukuk market shows strong growth and expanding reach. It reflects rising demand for Islamic finance products worldwide. Sukuk bonds attract investors seeking Sharia-compliant options and asset-backed securities. Understanding global trends helps grasp the future of sukuk issuance and investment.
Growth In Islamic Finance
Islamic finance has grown rapidly over the past decade. Sukuk issuance has increased as countries and companies seek halal funding. This growth supports economic development in Muslim and non-Muslim countries. It also diversifies financial markets and offers alternatives to conventional bonds.
Regional Market Leaders
Malaysia leads the sukuk market with strong government support. Saudi Arabia follows with large sovereign sukuk issuances. The UAE and Indonesia also show rising activity. These regions attract investors with robust legal frameworks and active financial hubs.
Future Outlook
The sukuk market is expected to expand further in the coming years. New sectors like green sukuk and infrastructure financing gain attention. More countries may introduce regulations to support sukuk growth. This will create new opportunities for investors and issuers globally.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/sukuk.asp_final-1bd6a7cff61f44c78882e54a48d9fe3d.png)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Are Sukuk Structured?
Sukuk are structured as asset-backed certificates representing ownership in tangible assets. Investors earn returns from the asset’s income, sharing risks and profits. The structure complies with Sharia law, avoiding interest, and uses contracts like Ijarah, Murabaha, Mudarabah, or Musharakah to ensure Islamic finance principles.
What Are Sukuk Bonds?
Sukuk bonds are Islamic financial certificates representing ownership in assets. They comply with Sharia by avoiding interest and sharing profits. Investors earn returns from underlying asset performance, not fixed interest. Sukuk provide a Sharia-compliant alternative to conventional bonds through asset-backed investment structures.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Sukuk?
Sukuk may have limited market liquidity and complex structures. Creditworthiness affects investor appeal. Regulatory differences can increase costs and risks. Asset backing may restrict flexibility compared to conventional bonds.
Are Sukuk Bonds Halal?
Sukuk bonds are halal as they represent ownership in assets, not interest-bearing debt. They comply with Sharia by sharing profit and risk from real assets. Independent Islamic scholars review their structure to ensure Sharia compliance, making sukuk a permissible investment under Islamic law.
Conclusion
Sukuk bonds offer a unique way to invest while following Islamic law. They provide ownership in real assets, avoiding interest payments. Investors share both profits and risks based on asset performance. This structure makes sukuk different from regular bonds. Understanding how sukuk works helps investors make informed choices.
The clear link to tangible assets builds trust and transparency. Overall, sukuk bonds combine ethical finance with practical investment benefits. They continue to grow as a valuable option in global markets.
