Have you ever wished you could delegate important tasks to someone you trust, freeing up your time and ensuring the job gets done right? That’s exactly what the Wakalah concept is all about.
It’s a simple yet powerful idea where you, as the principal, appoint an agent to act on your behalf for specific tasks you can’t or don’t want to handle yourself. Whether it’s managing a business deal, handling investments, or selling an asset, Wakalah gives you the freedom to rely on experts while staying in control.
You’ll discover how Wakalah works, its key elements, and why it’s becoming a trusted tool in finance and everyday life. Ready to learn how this concept can make your life easier and smarter? Let’s dive in.

Credit: www.freepik.com
Wakalah Basics
Understanding the basics of Wakalah helps clarify its role in Islamic finance and daily transactions. This concept involves trust and delegation between two parties. It allows one person to act on behalf of another, following clear rules and responsibilities.
Wakalah is simple yet powerful. It supports various activities, from business deals to personal tasks. Knowing its foundation ensures proper use and benefits for everyone involved.
Definition And Purpose
Wakalah is an Islamic agency contract. It allows a principal to appoint an agent to perform tasks. The agent acts in the principal’s name and interest. This contract is based on trust and permission.
The purpose is to delegate duties that the principal cannot handle. Reasons may include lack of time, skills, or knowledge. Wakalah helps complete tasks efficiently and legally under Islamic law.
Roles Of Principal And Agent
The principal is the person who gives authority. They decide what the agent should do. The principal remains responsible for the results and outcomes.
The agent, also called wakeel, accepts the role to act. The agent follows instructions and works honestly. They must avoid conflicts and keep the principal informed.
Both parties must agree clearly on duties and limits. This agreement prevents misunderstandings and ensures smooth cooperation.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Core Elements
The Wakalah concept revolves around a clear contract between two parties. It sets a foundation for trust and responsibility in Islamic finance. Understanding its core elements helps grasp how this agency works smoothly and fairly. These components define the roles and the agreement involved.
Principal (muwakkil)
The principal, called Muwakkil, is the person who gives authority. This person hires the agent to act on their behalf. The principal must be clear about what they want the agent to do. They hold the right to monitor and approve the agent’s actions.
Agent (wakeel)
The agent, known as Wakeel, carries out tasks for the principal. The agent must act honestly and follow the principal’s instructions. Their role is limited to what the principal allows. Trustworthiness and competence are key for the agent’s role.
Offer And Acceptance
The contract begins with an offer from one party. The other party must accept this offer clearly. This mutual agreement forms the basis of the Wakalah contract. Both parties should understand and agree on the terms fully.
Subject Matter
The subject matter is the task or service assigned to the agent. It must be lawful and clearly defined. Both parties should know exactly what the agent will do. This clarity prevents future disputes and ensures smooth execution.
Types Of Wakalah Contracts
Wakalah contracts are an important part of Islamic finance. They allow one person to appoint another to act on their behalf. This delegation helps in managing tasks that require expertise or authority. There are two main types of Wakalah contracts. Each serves a different purpose and offers unique benefits.
General Wakalah
General Wakalah gives the agent broad authority. The agent can handle many tasks without needing specific approval each time. This type is useful when the principal trusts the agent’s judgment fully. It saves time and makes decision-making faster. The agent acts in the best interest of the principal at all times.
Specific Wakalah
Specific Wakalah limits the agent’s authority to a particular task. The agent can only act on what the contract states. For example, selling a car or managing a single investment. This helps control risks and keeps the agent focused. The principal can clearly define the agent’s duties and powers.
Wakalah In Islamic Finance
Wakalah in Islamic finance is a contract where one party appoints another as an agent. The agent performs tasks on behalf of the principal, following clear instructions. This contract promotes trust and transparency, aligning with Islamic financial principles.
Wakalah allows clients to delegate tasks they cannot handle personally. It suits banking, investment, and real estate sectors. Understanding Wakalah helps grasp its vital role in Islamic finance.
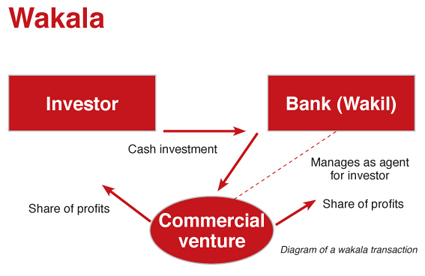
Agency Role In Banking
Banks act as agents for customers under Wakalah contracts. They manage funds, execute transactions, and provide services. This role helps banks serve clients efficiently while respecting Shariah rules. Customers trust banks to handle their money responsibly.
Investment And Asset Management
Wakalah empowers investors to appoint managers for asset growth. Managers invest funds in Shariah-compliant ventures. They act within agreed guidelines to protect client interests. This arrangement ensures professional handling of investments with ethical oversight.
Real Estate Transactions
In real estate, Wakalah enables agents to buy or sell properties for clients. Agents follow client instructions strictly in these deals. This method simplifies complex transactions and safeguards client rights. It supports transparent and fair property dealings under Islamic law.
Benefits Of Wakalah
Wakalah offers many benefits in business and finance. It allows one person to appoint another as an agent to act on their behalf. This concept saves time and effort. It creates clear roles and responsibilities. Wakalah builds confidence between parties and ensures tasks are done properly.
This system works well in various sectors, especially Islamic finance. It supports ethical and transparent dealings. Here are some key benefits of Wakalah.
Building Trust
Wakalah helps build strong trust between the principal and agent. The principal knows the agent must act responsibly. Both parties agree on clear terms and duties. This reduces misunderstandings and conflicts. Trust grows as the agent performs tasks faithfully. It creates a smooth and reliable working relationship.
Delegating Expertise
Wakalah allows the principal to delegate tasks to an expert. The agent often has more knowledge or skills in a certain area. This leads to better decision-making and results. Delegating saves the principal’s time and effort. It also ensures that specialized work is done correctly. The principal can focus on other important matters.
Ensuring Compliance With Shariah
Wakalah supports compliance with Islamic law, or Shariah. The agent acts within the rules set by the principal and Shariah principles. This prevents prohibited actions or investments. It promotes fairness, transparency, and ethical behavior. Shariah compliance is crucial in Islamic banking and finance. Wakalah ensures that all actions meet these religious requirements.
Credit: www.financialislam.com
Conditions And Rules
The Wakalah concept involves a contract where one person authorizes another to act on their behalf. This arrangement requires clear conditions and rules to ensure trust and legality. These rules protect both the principal and the agent. They clarify the rights and duties of each party. Understanding these conditions helps avoid misunderstandings and disputes.
Legal Capacity And Consent
Both the principal and the agent must have legal capacity. They must be of sound mind and legally able to contract. Consent must be given freely without pressure or deception. The agreement must be clear and understood by both parties. If either party lacks capacity or consent, the contract may be invalid.
Scope Of Authority
The agent’s authority must be clearly defined in the contract. It can be limited to specific tasks or broad enough for various actions. The principal decides what powers the agent holds. The agent cannot act outside this scope without permission. Any actions beyond the agreed scope may not bind the principal.
Fee And Compensation
The agent may receive a fee or compensation for their services. This fee should be agreed upon before the contract starts. It can be fixed or based on the results of the task. Transparency about fees prevents disputes later. If no fee is agreed, the agent may work voluntarily.
Challenges And Solutions
The Wakalah concept offers a clear way to delegate tasks. It allows principals to appoint agents for specific duties. Despite its benefits, challenges exist. These challenges require careful handling to keep the system fair and efficient.
This section explores common issues and practical solutions. It focuses on managing conflicts of interest, ensuring transparency, and handling risks well. Each area is vital for Wakalah’s success.
Managing Conflicts Of Interest
Conflicts of interest arise when agents act for their benefit, not the principal’s. This can harm trust and damage the relationship. Clear rules must guide agents to avoid such conflicts. Regular audits and monitoring help detect issues early. Training agents on ethical behavior supports fairness. Setting strict boundaries keeps the agent focused on the principal’s goals.
Ensuring Transparency
Transparency builds trust between the principal and the agent. It means sharing clear, honest information about actions and decisions. Agents should provide regular updates on progress and outcomes. Written agreements must clearly define roles and responsibilities. Open communication channels allow principals to ask questions anytime. Transparent processes reduce misunderstandings and disputes.
Risk Management
Risk is part of any Wakalah contract. Both principals and agents face financial and operational risks. Identifying risks early helps prepare for them. Contracts should include terms for risk sharing and mitigation. Insurance or guarantees can protect against losses. Agents must follow best practices to minimize errors. Effective risk management ensures stability and confidence in Wakalah agreements.
Practical Examples
Wakalah is a flexible concept used in many real-life situations. It allows a person or institution to act as an agent for another. The agent performs tasks the principal cannot do alone. Below are practical examples of how Wakalah works in different areas.
Bank As Agent In Property Deals
Banks often act as agents in property transactions. A client appoints the bank to buy or sell property. The bank handles the paperwork and negotiations. This saves time and ensures the deal follows all rules. The bank works for the client’s best interest. The client trusts the bank to complete the deal properly.
Wakalah In Investment Funds
Investment funds use Wakalah to manage client money. The fund manager acts as an agent for investors. They invest the money in stocks, bonds, or real estate. The manager follows clear instructions from the investors. This setup gives investors professional handling of their funds. Investors benefit from expert decisions without direct involvement.
Wakalah In Business Transactions
Businesses use Wakalah to delegate specific tasks to agents. An agent might handle sales, purchases, or contracts. The business owner gives clear limits to the agent’s authority. This helps complete tasks faster and with expert help. The agent reports back to the owner regularly. It creates trust and smooth operation in business.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Concept Of Wakalah?
Wakalah is an Islamic contract where a principal appoints an agent to perform specific tasks on their behalf. The agent acts with the principal’s authorization to complete defined duties efficiently. This agency model is widely used in finance, business, and legal transactions to delegate authority.
What Is The Wakalah Model With Example?
The Wakalah model is an agency contract where a principal appoints an agent to perform a specific task. For example, an owner authorizes an agent to sell their car at a set price.
What Are The Pillars Of Wakalah?
The pillars of Wakalah are the principal (muwakkil), the agent (wakil), the offer and acceptance, and the subject matter (muwakkal bihi).
What Are Some Examples Of Wakalah In Banking?
Examples of wakalah in banking include banks acting as agents to buy or sell property and invest clients’ assets in real estate. Banks also manage funds and execute transactions on clients’ behalf under wakalah contracts.
Conclusion
Wakalah offers a clear way to delegate tasks with trust. It helps principals save time and use expert agents. This concept fits well in finance and business dealings. Agents act within set limits and follow client instructions. Understanding Wakalah can improve how you manage responsibilities.
It builds cooperation and clarity between parties involved. Simple and effective, Wakalah supports smooth transactions. Embracing this concept can lead to better decision-making.
